How to Analyze Earnings Reports?
Debt-to-equity ratio
Previously, we have walked you through some basic financial ratios, such as the current ratio, which reveals - How do I avoid buying shares of a company that might go bankrupt?
In this chapter, we will guide you to find out what other factors can we use to identify risky investments.
Why we need D/E ratios?
When investors perform due diligence before investing, many amateur players simply glance at the top line (revenue) and the bottom line (profit/earning) on the income statement.
But one fact is often ignored: What if a lot of debt was used to finance growth?
If the cost of borrowing is greater than the income generated, the company share value will decline.
So how do we know if the target company is borrowing just right or too much? Here comes the 「debt-to-equity ratio」.
What is the debt-to-equity (D/E) ratio?
The debt-to-equity (D/E) ratio is used to measure a company's financial leverage and is calculated by dividing a company’s total liabilities by its shareholder equity.
For example, if company A has $500,000 in total liabilities and $250,000 in total stockholders’ equity, your debt-to-equity ratio is 2. This means you use $2 in debt for every $1 of equity.
What is a good D/E ratio?
Acceptable debt-to-equity ratios differ among industries.
In general, a ratio that is greater than the industry average is too high. If the industry average is 0.9, company A is one of the companies with a high debt-to-equity ratio.
What are the disadvantages of high D/E ratios?
- Increased risk of going bankrupt
High debt level can overburden a company with high interest payments. If the firm cannot generate enough business to pay back, creditors can take over the company's assets and force it into bankruptcy.
- Reduced shareholder ownership
A debt-to-equity ratio increase means a reduction in the value of owners’ stake in a business as a proportion of its assets. If the company sells to liquidate, more proceeds will be distributed to debtholders.
- Trouble obtaining additional financing
Say if the bank cutoff is 1.4 and the company’s D/E ratio is 2, it would deny the company any loans.
Which industries tend to have high D/E ratios?
- Banking and financial services sector
- Airline industry
- Large manufacturing companies
- Other capital-intensive industries
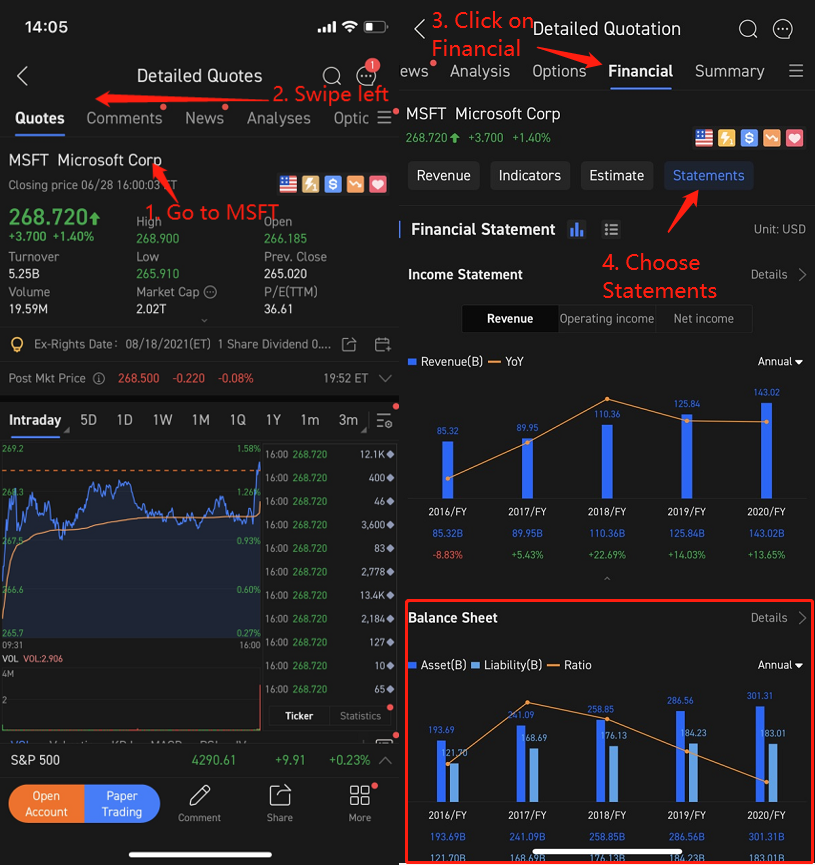
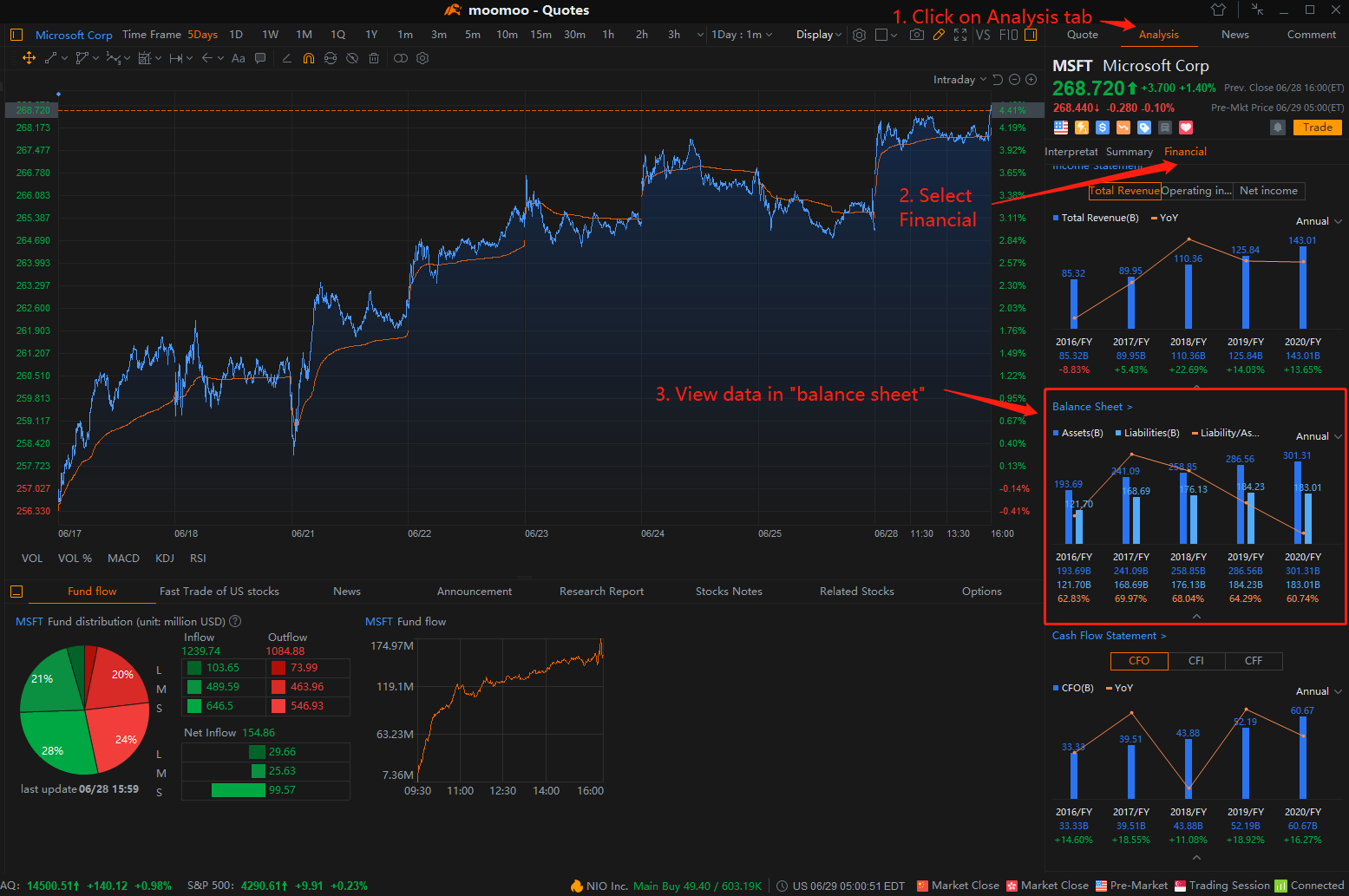
How to find data in moomoo?
For desktop users:
For mobile app users: