What Is Buying on Margin?
Buying on margin is the act of buying securities, such as stocks, bonds, or futures contracts, using money borrowed from a broker. The borrower then uses the securities as collateral for the loan. For example, let's say you wanted to buy $1,000 worth of stock but only had $500. If you were buying on margin, you could borrow the other $500 from your broker. The specifics of buying on margin vary from broker to broker, but the basic idea is that you use the borrowed money to increase your investment.
Buying on margin is generally considered a high-risk investment strategy because it allows investors to control a large position with a relatively small amount of money down. This leverage can lead to large losses if the underlying security price falls. For this reason, most brokerages require that investors who want to buy on margin meet certain criteria. Such as maintaining a minimum account balance and/or meeting certain asset requirements. Although it can be risky, buying on margin can also be a good way to increase your return potential if used correctly.
Key Takeaways:
Buying on margin is when an investor buys an asset, usually stock, by borrowing money from a broker.
If the security value falls below a certain level, known as a margin call. The investor may be required to post additional collateral.
Things You Should Know About Buying on Margin
The Federal Reserve Board sets the margin requirements for investors. As of 2019, you will need to fund at least 50% of your purchase price with cash and may borrow another fifty percent from brokers or dealers if needed!
Investors purchase securities on margin and essentially borrow money from their broker to finance part of the transaction. The securities serve as collateral for the loan, and the investor pays interest on the amount borrowed.
The initial margin requirement is the percentage of the total purchase price that must be funded with cash. For stocks, suppose the initial margin requirement is currently 50%. So, if an investor wants to buy $700 worth of stock, they would need at least $350 in cash and could borrow the other $350 from their broker.
The requirement of maintenance margin is the minimum amount of equity that must be maintained in a margin account. It is calculated as a percentage of the total value of the securities in the account. Let's look at an example, if the maintenance margin requirement is 50%, the value of the securities in the account must remain above 50% of the original value for the account to stay open. If the value of the securities falls below this level, a margin call will be issued. And the account holder will be required to deposit additional funds or sell some of the securities to bring the account back up to the required level.
How Buying on Margin Works?
Buying on margin begins when an investor contacts a broker and asks to open a margin account. The lenders usually requires the borrowers to pay interest on the loan and a maintenance fee. One important factor when deciding if to buy on margin is the margin interest rate charged by the broker. The higher the margin interest rate, the more expensive it will be to borrow money. Another important factor is the Maintenance Margin Requirement (MMR), which is the minimum amount of equity an investor must maintain in their account in order to avoid a Margin Call.
The MMR can vary depending on the broker but is typically around 30-40%. For example, if an investor has a $10,000 stock portfolio and purchases $5,000 worth of additional shares using margin, their MMR would be 50% ($5,000/$10,000). If the value of their portfolio falls below $7,500 (30% of $10,000), they will receive the Margin Call and will be required to either add more money to their account or sell some of their holdings. When investing on margin, it's important to remember that you are essentially borrowing money and that you may lose more money if the price of the asset falls. Nevertheless, buying on margin can help investors magnify their returns if used carefully.
How to Buy on Margin?
If you are interested in buying on margin, the first step is to open a margin account with a broker. Once your account is approved, you then need to deposit the initial margin requirement, typically 50% of the purchase price. For example, if you would like to buy $1,000 worth of stock, you will need to deposit $500 into your account.
Once the funds are deposited, you could place an order to buy the securities you want. The broker will then loan you the remaining amount needed to complete the purchase, up to the limit set by the Federal Reserve Board.
It's important to remember that you are responsible for any losses incurred on loan, so it's important to only borrow an amount you are comfortable with. In addition, you will be required to pay interest on the loan and any fees charged by the broker.
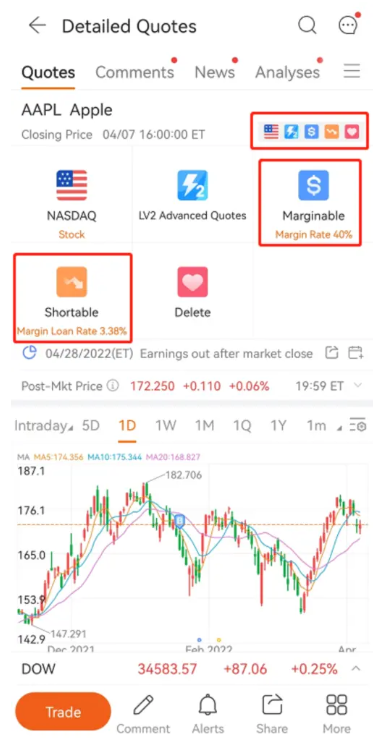
The margin account of moomoo trading app identifies which stocks are marginable and shortable, along with the margin and loan rates. You could decide if you would like to buy on margin.
Why Should You Invest on Margin?
There are reasons why you might want to invest on margin:
1) Magnify Your Returns:
Investing on margin can be a good way to do it if you're looking to magnify your returns. When you invest on margin, you're essentially borrowing money to invest with, which can help you increase the size of your position and potentially multiply your profits if the investment goes in your favor. Of course, this may also means that your losses could be amplified as well if the investment doesn't perform as expected. So, it's important to carefully consider the risks before taking this step.
2) Generate Additional Income:
Another reason to invest on margin is to generate additional income. If you have some cash in your account that you're not currently using, you can put it to work by investing on margin. Doing so can earn interest on the money you're borrowing, which can help offset some of the costs associated with margin investing.
3) Take Advantage of Opportunities:
Investing on margin can also give you the opportunity to take advantage of investment opportunities that you might otherwise miss out on. For example, if there's a stock that you're interested in but can't afford to buy outright, investing on margin may allow you to get in at a lower price point. This flexibility can be helpful when trying to build a diversified portfolio.
4) Hedge Against Risk:
Lastly, some investors use margin as a way to hedge against risk. For example, if you have a portfolio of stocks that are currently losing value, investing on margin in an effort to recoup your losses may be an option worth considering. Of course, there's always the potential for further losses when investing, so it's important to approach this strategy with caution.
Margin investing comes with unique risks and rewards, so it's important to do your homework before taking this step. However, for investors who accept to take on a bit more risk, investing on margin may be a good way to boost returns and take advantage of opportunities that might otherwise be out of reach.

Once you do margin trading on the moomoo app, moomoo's risk account details page will show your account risks, disposal suggestions, and early warning information based on fluctuations of the individual stocks you hold.