Google Q4 2023 Earnings Review: Limited Upside Potential
Alphabet, the parent company of Google, announced its fourth-quarter earnings after the US stock market closed on Tuesday. The company achieved revenue of $86.31 billion in the fourth quarter, a 13% increase year-over-year, exceeding the Bloomberg consensus estimate of $85.36 billion. Adjusted earnings per share were $1.64, higher than the expected $1.59. Despite revenue and profit surpassing expectations, the stock price performed poorly post-earnings.
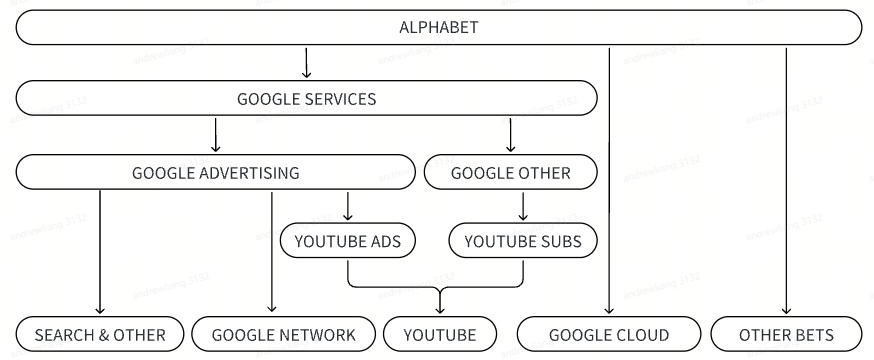
I. Advertising is the pillar of Google's business, and cloud computing is the key growth driver
Alphabet, the parent company of Google, operates in two main segments: Google and Other Bets (innovative businesses). Google has a wide range of businesses, with its revenue mainly coming from Google Services and Google Cloud.
- Google Services include advertising revenue and other revenues. Advertising revenue accounts for over 80% of Google's total revenue, contributing the core source of income. It can be divided into search advertising, Network advertising, and YouTube advertising, with respective revenue shares of around 60%, 10%, and 10%. Google Services' other businesses mainly include YouTube's non-advertising business (mainly user subscriptions) and hardware products like Pixel, Fitbit, Google Nest home devices, and Google Play.
- Google Cloud can be divided into Google Cloud Platform and Google Work Space, providing cloud services and office collaboration tools.
Advertising business is Google's foundation with high dependency, determining the overall performance; whereas Google Cloud is the key growth driver, reflecting the cloud business demand driven by AI, and relates to Google's position in the new round of AI competition. Both are indispensable for the stock's post-earnings performance.
Chart: Google Business Structure
II. Advertising Performance Not Bad, But Market Expectations Were Higher
Google's overall advertising business achieved revenue of $65.51 billion in the fourth quarter, a year-over-year increase of 10.97%, slightly below the market's expectation of $65.77 billion (+11.4%).
In reality, we believe that the advertising business performance this quarter was not poor, as the quarter-over-quarter growth rate continued to rise. The shortfall in expectations is more due to the fact that Google's advertising revenue had already exceeded expectations by a substantial margin in the previous two quarters, coupled with an improving consumer environment in the fourth quarter, prompting the market to continuously revise its outlook for the recovery of the advertising business, and thus raising expectations for Google's advertising revenue.
Chart: Google Quarterly Advertising Revenue (in million USD)

Looking at the breakdown of the advertising business, YouTube advertising continued to perform exceptionally well, exceeding expectations. YouTube's advertising revenue was $9.2 billion, with a quarter-over-quarter increase of 16%, driven by growth in connected TV viewership.
YouTube content has strong appeal to users, with viewing time continuing to increase throughout the quarter. Looking at the market share of major streaming services, cable television saw an increase in overall market share in the fourth quarter due to a large number of sports broadcasts, squeezing the market share of streaming media. However, compared to its peers, YouTube's market share within streaming media remained relatively stable.
YouTube's continued improvement in monetization rates also contributed to revenue growth, with monetization including subscription fees and advertising. In July, Google raised the subscription prices for YouTube Music and Premium. On the advertising side, in 2023, YouTube introduced formats such as 30-second non-skippable ads and ad pauses. Furthermore, in the fourth quarter, YouTube actively promoted the use of ad blockers, requiring users to disable ad blockers in order to play videos, thus encouraging users to switch to ad-free premium memberships.
Chart: Major Streaming Services Market Share

Search Advertising Business Shows Robust Growth, with Search Ad Revenue at $48 Billion, Up 9% Quarter-Over-Quarter. In the medium to short term, Google Chrome browser maintains a stable market share, and Bing has not made a significant impact on Google Search. According to Statcounter data, as of the fourth quarter, Google Search Engine's market share slightly increased to 91.62% (from 91.58% at the end of the third quarter), while Microsoft's Bing market share increased from 3.01% to 3.37%.
Network Advertising Revenue Decreased by 2% Year-Over-Year, which typically refers to advertising content placed on third-party websites through advertising products such as Google AdSense and Google Ad Manager. However, with an 8.2% increase quarter-over-quarter, this is not considered a significant issue.
Chart: Major Search Engine Market Share

III. The Increase in AI Costs Limits Cost Reduction Effects
The gross margin slightly declined to 56.5% quarter-over-quarter in Q4, and the operating profit margin decreased to 27.4% quarter-over-quarter.
Google's cost reduction measures for 2023 primarily include layoffs and cutting office expenses, as well as optimizing expenditures through extending the depreciation period for servers (from 4 years to 6 years), the latter of which is mainly a paper-based cost reduction through financial means rather than an actual cost decrease.
Starting from the first quarter, Google has been continuously implementing cost-saving and efficiency measures such as layoffs, but the impact on overall cost savings is limited, and it is more of an adjustment in cost structure. This is because most of the positions eliminated have been replaced by more expensive AI engineers. Compared to Meta, Google's cuts are also relatively mild. By the end of the third quarter, the total number of employees at its parent company only decreased by 4% compared to the end of 2022, while Meta Platforms' reduction was 23%. The expense of stock-based compensation also increased year-over-year, with the total cost of stock incentives increasing from $19.3 billion in 2022 to $22.4 billion for the year.
Chart: Google's Cost Reduction Plan

Moreover, looking at R&D expenses and capital expenditures, Google's investment in AI significantly increased in the fourth quarter. R&D expenses grew by 18% year-over-year, with a notable acceleration in growth rate. Considering the total capital expenditures from Q1 to Q3 of 2023, the capital expenditures for the first three quarters decreased by 11.1% year-over-year, due to some projects being delayed. Q4 capital expenditures were $11 billion, up 45% year-over-year, primarily driven by investments in infrastructure, and the overall capital expenditures were higher than in 2022.
Chart: Google's Quarterly Capital Expenditure (in Million USD)

IV. Google Cloud Performance Slightly Exceeds Expectations, But Still Not Enough
The revenue growth rate of Google Cloud is crucial as it primarily reflects the demand pull from AI needs for cloud computing. In the fourth quarter, Google's cloud business revenue was $9.1 billion, with a year-over-year increase of 25.6%, better than the expected 22%, and showed a stable rebound compared to the previous quarter.
Chart: Google Cloud Revenue and Growth Rate (in Million USD)

However, this growth rate is still not satisfactory for two main reasons. Firstly, the market's expectations were not high to begin with; a 22% year-over-year growth rate is basically on par with the previous quarter. After Google Cloud's growth rate fell below expectations last quarter, the market intentionally lowered its growth expectations for Google Cloud. Secondly, this performance is weak compared to the 30% growth rate reported by Microsoft on the same day. Given that Google Cloud's size is smaller than Amazon and Microsoft, the market typically has higher expectations for its growth rate.
Chart: Market Share of Major Cloud Computing Providers

From the performance in recent quarters, Microsoft Cloud has benefited from incremental demand brought by AI, making its growth curve smoother, even showing an acceleration last quarter. As for Google, the release of Gemini came later, and it is currently in the process of catching up with ChatGPT. Google does not have the TO C-side advantage of office software like Microsoft, and the incremental demand brought by AI is mainly aimed at TO B customers, which means the benefits for Google Cloud will come later and at a slower pace than for Microsoft Azure.
V. How Do We View Google's Future?
1. EPS Growth
We continue to look at both advertising and Google Cloud businesses.
(a) Advertising Business: Expected to maintain good growth in 2024, with YouTube remaining the strongest growth sector in advertising.
On the macro front, according to WARC's 2023/24 global advertising spending forecast, global advertising spending is expected to reach $963.5 billion by the end of 2023, with a year-over-year growth of 4.4%. Ad spending is expected to accelerate in 2024, with a projected growth of 8.2% year-over-year, with the upcoming U.S. Presidential election and the Olympics (scheduled for 2024) helping to offset macro uncertainties in advertising.
The search business is expected to maintain steady growth in 2024. Google's position in search is difficult to challenge in the short to medium term, and it's more likely that we'll see Microsoft and Google squeezing out smaller search engine market shares. Even if New Bing increases its user search volume, advertisers are unlikely to shift their budgets quickly until the number of new users reaches a significant scale, preferring to use Google's AI tools like PMAX to influence ad placements.
(b) Google Cloud Growth Expected to Stabilize and Rebound
Looking at the growth rates of Amazon and Google over the past two quarters, there are signs of a growth rebound. The trend of corporate IT spending cuts is slowing, and cloud computing is expected to stabilize and rebound in 2024.
(c) Costs are Still Expected to be Significant
According to company guidance, overall capital expenditures in 2024 will be higher than in 2023, meaning the company will continue to increase capital and R&D investment. The marginal effect of cost reduction and efficiency will decrease quarter-over-quarter, meaning there won't be significant improvements in costs and expenses in 2024.
Based on these assumptions, we expect operating revenue to grow by 14% year-over-year to $350.7 billion in 2024, and due to increased costs, net profit is expected to grow by 12% year-over-year to $82.6 billion.
2. Shareholder Return
In April 2023, Google announced a $70 billion buyback program (also $70 billion in 2022), with $61.5 billion repurchased throughout Q4 of 2023. Assuming a buyback of $60 billion in 2024, the shareholder yield at the current market value is about 3.1%.
3. Valuation
Google's free cash flow for the full year of 2023 was $69 billion, and net profit was $73.7 billion. The current market value is equivalent to 27 times the free cash flow and 26 times the net profit. Based on the forecasted net profit for 2024, this corresponds to 23 times the predicted net profit for 2024. Looking at the valuation range over the past five years, the midpoint is around 26 times, meaning that Google's current valuation upside is not too large (about 12%).
4. Risks
The current valuation is also related to several pending antitrust risks concerning Google. Let us analyze the impact specifically:
(a) Google Play Tax: Google lost a lawsuit to Epic and agreed to allow users to download software through third-party channels and also to offer a third-party payment system. Google's revenue does not break down this specific business line, but according to Sensor Tower data, app sales on Google Play in 2023 were approximately $38.5 billion, with a combined fee rate of about 27%. Since third-party payments may also incur channel fees, and small developers are less likely to develop their own systems, it's estimated that if 20% of developers choose to bypass the Google tax, the impact would be around $2 billion, representing less than 1% of Google's total revenue in 2023, which is a limited impact.
(b) Google's Search Monopoly Case: Set to go to trial in September 2023 and expected to last 10 weeks, the federal court believes that iPhone's Safari defaulting to Google as the search engine could be monopolistic, with Google paying a share to Apple in exchange for this position. The specific revenue Google derives from iPhone's Safari searches is unknown, and if unbundling occurs, it may affect a small portion of search advertising revenue, but at the same time, it would also reduce the share paid to Apple. However, given that Google Search has already captured the minds of users, it's presumed that the impact on this portion of revenue would be within manageable limits.
Overall, Google's financial report is not particularly poor, and the significant post-earnings drop in stock price suggests that investors have higher expectations for growth, given that valuations in the tech sector are not low. Google is still poised to benefit from the demand driven by AI this year, with related applications expected to gradually commercialize. However, unlike last year, investors will be more focused on tangible performance improvements brought by AI this year. Given the current valuation, Google's upside potential appears limited. Until there is a clear contribution to earnings or new catalysts, the stock price is expected to consolidate.
Disclaimer: Community is offered by Moomoo Technologies Inc. and is for educational purposes only.
Read more
Comment
Sign in to post a comment