Is SATS (SGX:S58) Using Too Much Debt?
Is SATS (SGX:S58) Using Too Much Debt?
Warren Buffett famously said, 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. Importantly, SATS Ltd. (SGX:S58) does carry debt. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
沃伦·巴菲特曾说过一句名言:“波动性远非风险的代名词。”当你检查公司的资产负债表的风险时,考虑它的资产负债表是很自然的,因为企业倒闭时通常会涉及债务。重要的是,SATS有限公司(新加坡证券交易所股票代码:S58)确实有债务。但是,股东是否应该担心其债务的使用?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
为什么债务会带来风险?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
一般而言,只有当公司无法通过筹集资金或用自己的现金流轻松还清债务时,债务才会成为真正的问题。在最坏的情况下,如果公司无法向债权人付款,它可能会破产。但是,更常见(但仍然昂贵)的情况是,公司为了控制债务,必须以低廉的股价稀释股东。当然,债务的好处在于它通常代表廉价资本,尤其是当它以高回报率进行再投资的能力取代公司的稀释时。当我们考虑公司使用债务时,我们首先将现金和债务放在一起考虑。
What Is SATS's Debt?
什么是SATS的债务?
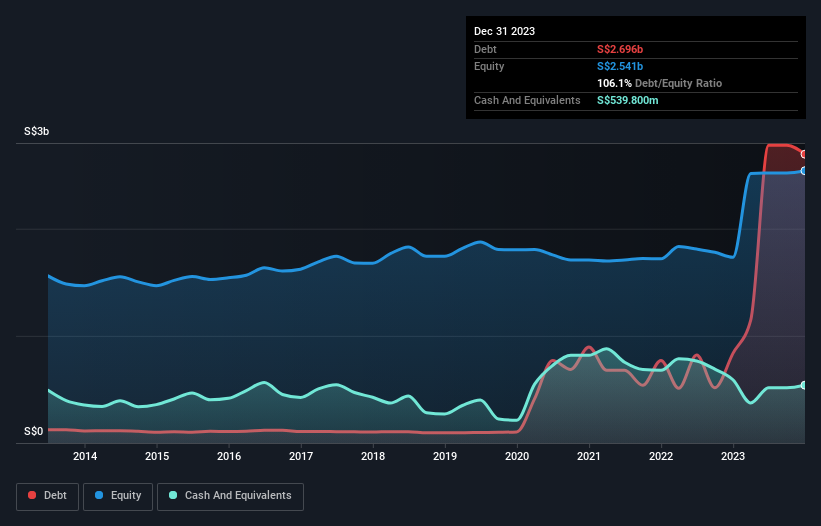
As you can see below, at the end of December 2023, SATS had S$2.70b of debt, up from S$836.9m a year ago. Click the image for more detail. However, because it has a cash reserve of S$539.8m, its net debt is less, at about S$2.16b.
如下所示,截至2023年12月底,SATS的债务为27.0亿新元,高于去年同期的8.369亿新元。点击图片查看更多细节。但是,由于其现金储备为5.398亿新元,其净负债有所减少,约为21.6亿新元。
How Healthy Is SATS' Balance Sheet?
SATS 的资产负债表有多健康?
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that SATS had liabilities of S$3.33b due within 12 months and liabilities of S$2.70b due beyond that. On the other hand, it had cash of S$539.8m and S$1.15b worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by S$4.33b.
放大最新的资产负债表数据,我们可以看到,SATS的负债为33.3亿新元,12个月后到期的负债为27.0亿新元。另一方面,它有5.398亿新元的现金和价值11.5亿新元的应收账款将在一年内到期。因此,其负债超过其现金和(短期)应收账款总额43.3亿新元。
When you consider that this deficiency exceeds the company's S$3.79b market capitalization, you might well be inclined to review the balance sheet intently. Hypothetically, extremely heavy dilution would be required if the company were forced to pay down its liabilities by raising capital at the current share price.
当你考虑到这一缺口超过了公司37.9亿新元的市值时,你很可能会倾向于仔细审查资产负债表。假设,如果公司被迫通过按当前股价筹集资金来偿还负债,则需要进行极其严重的稀释。
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
我们通过以下方法来衡量公司的债务负担与其盈利能力:将其净负债除以利息、税项、折旧和摊销前的收益(EBITDA),并计算其利息和税前收益(EBIT)支付利息支出(利息保障)的难易程度。这种方法的优势在于,我们既考虑了债务的绝对数量(包括净负债与息税折旧摊销前利润),也考虑了与该债务相关的实际利息支出(及其利息覆盖率)。
While SATS's debt to EBITDA ratio (3.8) suggests that it uses some debt, its interest cover is very weak, at 1.5, suggesting high leverage. It seems that the business incurs large depreciation and amortisation charges, so maybe its debt load is heavier than it would first appear, since EBITDA is arguably a generous measure of earnings. So shareholders should probably be aware that interest expenses appear to have really impacted the business lately. However, the silver lining was that SATS achieved a positive EBIT of S$173m in the last twelve months, an improvement on the prior year's loss. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if SATS can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
尽管SATS的债务与息税折旧摊销前利润的比率(3.8)表明它使用了部分债务,但其利息覆盖面非常薄弱,为1.5,这表明杠杆率很高。看来该企业会产生巨额折旧和摊销费用,因此其债务负担可能比最初出现的要重,因为息税折旧摊销前利润可以说是衡量收益的丰厚指标。因此,股东可能应该意识到,最近利息支出似乎确实影响了业务。但是,一线希望是,SATS在过去十二个月中实现了1.73亿新元的正息税前利润,比去年的亏损有所改善。毫无疑问,我们从资产负债表中学到的关于债务的知识最多。但最终,该业务的未来盈利能力将决定SATS能否随着时间的推移加强其资产负债表。因此,如果您专注于未来,可以查看这份显示分析师利润预测的免费报告。
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So it's worth checking how much of the earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) is backed by free cash flow. Happily for any shareholders, SATS actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT over the last year. That sort of strong cash generation warms our hearts like a puppy in a bumblebee suit.
最后,企业需要自由现金流来偿还债务;会计利润根本无法减少债务。因此,值得检查一下利息和税前收益(EBIT)中有多少是由自由现金流支持的。令所有股东感到高兴的是,去年SATS产生的自由现金流实际上超过了息税前利润。这种强劲的现金产生像穿着大黄蜂套装的小狗一样温暖着我们的心。
Our View
我们的观点
Neither SATS's ability to cover its interest expense with its EBIT nor its level of total liabilities gave us confidence in its ability to take on more debt. But its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow tells a very different story, and suggests some resilience. We should also note that Infrastructure industry companies like SATS commonly do use debt without problems. When we consider all the factors discussed, it seems to us that SATS is taking some risks with its use of debt. So while that leverage does boost returns on equity, we wouldn't really want to see it increase from here. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. For example, we've discovered 2 warning signs for SATS (1 is significant!) that you should be aware of before investing here.
无论是SATS用息税前利润支付利息支出的能力,还是其总负债水平,都没有使我们对它承担更多债务的能力充满信心。但是它将息税前利润转换为自由现金流却讲述了一个截然不同的故事,也表明了一定的弹性。我们还应该注意,像SATS这样的基础设施行业公司通常会毫无问题地使用债务。当我们考虑所讨论的所有因素时,在我们看来,SATS在使用债务方面正在冒一些风险。因此,尽管这种杠杆率确实提高了股本回报率,但我们真的不希望看到它从现在开始增加。资产负债表显然是分析债务时需要关注的领域。但归根结底,每家公司都可以控制资产负债表之外存在的风险。例如,我们发现了 2 个 SATS 警告信号(1 个很重要!)在这里投资之前,您应该注意这一点。
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
归根结底,通常最好将注意力集中在没有净负债的公司身上。您可以访问我们的此类公司的特别名单(所有公司都有利润增长记录)。它是免费的。
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
对这篇文章有反馈吗?对内容感到担忧?直接联系我们。 或者,给编辑团队 (at) simplywallst.com 发送电子邮件。
Simply Wall St的这篇文章本质上是笼统的。我们仅使用公正的方法根据历史数据和分析师的预测提供评论,我们的文章无意作为财务建议。它不构成买入或卖出任何股票的建议,也没有考虑到您的目标或财务状况。我们的目标是为您提供由基本数据驱动的长期重点分析。请注意,我们的分析可能不考虑最新的价格敏感型公司公告或定性材料。简而言之,华尔街没有持有任何上述股票的头寸。
