All States Resilient With Some Exceeding GDP Growth Of 3.6% Last Year: DOSM
All States Resilient With Some Exceeding GDP Growth Of 3.6% Last Year: DOSM
In 2023, Malaysia's economy expanded moderately with all states recorded favourable positive growths for the year Malaysia's economy expanded by 3.6 per cent in 2023, reaching a GDP of RM1.6 trillion.
2023年,马来西亚经济适度扩张,所有的州在该年均实现了有利的正增长,马来西亚的经济增长了3.6%,达到1.6万亿令吉的GDP。
The Department of Statistics Malaysia (DOSM) released the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) By State, 2023 today which provides insights into sectoral perspectives and the economic contributions of each state to Malaysia's overall economic landscape.
马来西亚统计局(DOSM)今天发布了2023年州级国内生产总值(GDP)报告书,这为从产业和地区角度洞察每个州对马来西亚整体经济格局的经济产出做出了贡献。
These statistics ensued the national GDP released on May 17, 2024.
这些数据是继2024年5月17日发布全国GDP后跟进的。
DOSM said the Services sector continued to be the driving force of the national economy, contributing 59.2 per cent, grew 5.1 per cent as against 2022. Within the same period, the Manufacturing sector, holding its position as the second largest contributor to GDP, experienced modest growth of 0.7 per cent. Similarly, the Agriculture and the Mining & quarrying sectors experienced moderate growth of 0.7 per cent and 0.5 per cent, respectively.
DOSM表示,服务业仍然是推动国家经济发展的主要力量,贡献了59.2%,比2022年增长了5.1%。在同一时期内,制造业作为GDP第二大贡献者,出现了0.7%的适度增长。同样,农业和采矿业与采石业也分别出现适度0.7%和0.5%的增长。
The Construction sector, on the other hand, sustained its momentum, achieving continued growth of 6.1 per cent.
另一方面,建筑业保持了其发展势头,实现了6.1%的持续增长。
The Chief Statistician of Malaysia Dato' Sri Dr. Mohd Uzir Mahidin said, "At the state level, four (4) states surpassed the national growth rate which were Selangor at 5.4 per cent, Pahang 5.2 per cent, Johor 4.1 per cent, and W.P. Kuala Lumpur at 3.7 per cent.
马来西亚首席统计师Dato'Sri Dr. Mohd Uzir Mahidin表示:“在州一级,有四个州超越了全国增长率,分别是雪兰莪5.4%,彭亨5.2%,柔佛4.1%和吉隆坡联邦直辖区3.7%。
Nevertheless, Selangor, W.P. Kuala Lumpur, Johor, Sarawak, and Penang remained the primary contributors, collectively contributing 67.7 per cent to Malaysia's economy."
然而,雪兰莪州、吉隆坡、柔佛、砂拉越和槟城仍然是主要贡献者,共占马来西亚经济的67.7%。
The economic performance of Selangor, Pahang, and Johor was driven by the Services sector, followed by the Manufacturing sector. For Selangor and Johor, the expansion of its Services sector by 6.1 per cent and 5.4 per cent respectively were propelled by growth in Utilities, transport & storage, and information & communication subsectors.
雪兰莪州、彭亨州和柔佛州的经济表现是由服务业驱动的,其次是制造业。对于雪兰莪州和柔佛州来说,其服务业的扩张在运输和仓储、信息和通信子行业的增长推动下分别增长了6.1%和5.4%。
Meanwhile, Pahang's Services sector grew by 6.0 per cent, driven by Wholesale & retail trade, food & beverages, and accommodation.
与此同时,彭亨州的服务业增长了6.0%,得益于批发零售贸易、食品饮料和住宿。
In Selangor, the Manufacturing sector increased by 2.0 per cent, attributed to the expansion in Transport equipment, other manufacturing, and repair subsector (6.2%), as well as Vegetable and Animal Oils & Fats and Food Processing (10.3%). Johor's Manufacturing sector increased by 2.8 per cent, driven by growth in Electrical, electronic, and optical products (2.9%), while Pahang experienced a 6.7 per cent growth in Petroleum, chemical, rubber, and plastic products, contributing to a 2.1 per cent increase in the state's Manufacturing sector. Meanwhile, W.P. Kuala Lumpur achieved an economic growth of 3.7 per cent, largely impelled by its Services sector, which serves as the backbone of the state's economy. This sector expanded by 4.9 per cent, supported by Wholesale & retail trade, food & beverages, and accommodation.
在雪兰莪州,制造业增长了2.0%,归因于运输设备、其他制造和修理子行业(增长6.2%)以及植物和动物油脂和食品加工(增长10.3%)。柔佛州的制造业增长了2.8%,得益于电器、电子和光学制品(增长2.9%),而彭亨州的石油、化学、橡胶和塑料制品增长了6.7%,导致该州的制造业增长了2.1%。与此同时,吉隆坡联邦直辖区实现了3.7%的经济增长,主要得益于服务业,这是该州经济的支柱。该行业增长了4.9%,得到了批发零售交易,食品和饮料以及住宿的支持。
DOSM added, "Growth in the Services sector, especially in the Wholesale & retail trade, food & beverages and accommodation sector as well as Utilities, transport & storage and information & communication are able to compensate the decline of the Manufacturing sector in several states. The decline in this sector was attributed to lower production of Electrical, electronic, and optical products, primarily affected by weakened global demand, particularly for semiconductors, integrated circuits, and spare parts." Pulau Pinang, which is the country's main producer of electric and electronic products, recorded a fall in the Manufacturing sector at 0.5 per cent due to a 0.8 per cent drop in the production of the specific products.
DOSM补充说:“服务业的增长,特别是批发零售贸易、食品和饮料以及住宿部门以及公用事业、运输和仓储和信息和通信能够弥补多个州制造业的下降。该行业的下降归因于在全球需求疲软的情况下,特别是对于半导体、集成电路和备件的需求的下降。 作为马来西亚电器和电子产品的主要生产商,槟城的电器、电子和光学制品的生产下降了0.5%。
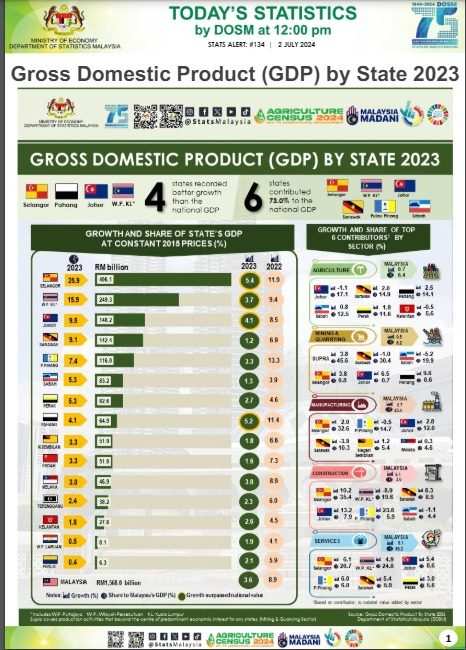
However, the growth in the Services sector at 6.0 per cent offset this fall, supporting Pulau Pinang's economic growth to expand at 3.3 per cent. Production of Electric, electronic, and optical products in Kedah, which was the country's fourth highest producer also showed a decline of 4.6 per cent, leading to a 3.2 per cent decrease in its Manufacturing sector. Nevertheless, the state's GDP increased to 1.6 per cent, driven by a 4.0 per cent growth in the Services sector, particularly supported by Wholesale & retail trade, food & beverages and accommodation which expanded by 5.3 per cent.
然而,零售业增长了6.0%,支撑了槟城经济增长了3.3%。全国第四大生产商吉打州电器、电子和光学制品的产量也下降了4.6%,导致其制造业下降了3.2%。然而,该州的GDP增长了1.6%,源自于服务业的增长,特别受到批发零售贸易、食品和饮料以及住宿行业的支持,增长了5.3%。
Similarly, expansions in the Services sector also have a significant impact on Kelantan's economy, which grew by 2.6 per cent. This sector expanded at 3.8 per cent, particularly contributed by the 5.8 per cent expansion in Wholesale & retail trade, food & beverages and accommodation sector, offsetting the fall in the Agriculture and Manufacturing sectors of 0.5 per cent and 2.6 per cent respectively.
同样,服务业的扩张也对吉兰丹州经济产生了重大影响,其经济增长了2.6%。该行业增长了3.8%,特别是批发零售贸易、食品和饮料以及住宿行业的增长推动,抵消了农业和制造业的下降,分别下降了0.5%和2.6%。
The Agriculture sector also plays an important role in driving the economic growth of the states, particularly in ensuring national food security. The strengthening of Melaka's economy to 3.0 per cent in 2023 was bolstered not only by a 4.2 per cent increase in the Services sector but also by a notable 6.5 per cent growth in the Agriculture sector. This sector's expansion helped mitigate the impact of modest growth in the Manufacturing sector (0.3%), due to the decline in Electrical, electronic, and optical products (-3.1%).
农业部门也在推动各州经济增长方面发挥着重要作用,特别是在确保国家食品安全方面起着关键作用。马六甲经济增长到3.0%,不仅得益于服务业的增长4.2%,而且还得益于农业部门增长了 notable 6.5%。该部门的扩张有助于缓解制造业的适度增长(0.3%)的影响,由于电器、电子和光学制品的下降(-3.1%)。
Terengganu's state economy expanded by 2.3 per cent, driven by a 3.1 per cent growth in the Services sector, particularly in Government services (3.8%) and Wholesale & retail trade, food & beverages, and accommodation (3.5%). The moderate growth was contributed by the Manufacturing sector which was the second largest contributor to the state's economy, posted a marginal growth of 0.2 per cent as compared to a resilient growth of 8.3 per cent growth in 2022.
登嘉楼州经济增长了2.3%,得益于服务业的增长3.1%,尤其是政府服务(3.8%)和批发零售贸易、食品和饮料以及住宿(3.5%)。这种适度的增长是由制造业实现的,该行业是该州经济的第二大贡献者,比2022年的强劲增长0.2%略微增长。
The slowdown was attributed by the Petroleum, chemical, rubber, and plastic products which grew 0.3 per cent, as against 8.7 per cent the previous year Within the same period, the economy of Perlis grew by 2.1 per cent, supported by a 2.3 per cent growth in the Services sector, notably influenced by a 4.1 per cent expansion in Government services. W.P. Labuan's GDP increased by 1.9 per cent, driven by a 2.2 per cent growth in the Services sector, particularly in Finance & insurance, real estate, and business services (1.6%), which are the key drivers of the region's economy.
本季度石油、化工、橡胶和塑料制品增长了0.3%,低于上一年的8.7%。同期,玻璃市的经济增长了2.1%,得益于服务业增长了2.3%,主要受到政府服务扩张了4.1%的影响。拉布安自治特区的GDP增长了1.9%,服务业增长了2.2%,特别是金融和保险、房地产和商业服务(1.6%),这些板块是该地域经济的主要推动力。
Meanwhile, Negeri Sembilan's economy grew by 1.8 per cent, propelled by Services sector (4.5%), particularly in Utilities, transport & storage, and information & communication, which increased by 5.5 per cent. The state moderate economic growth was also influenced by the marginal growth of its Manufacturing sector (1.2%), influenced by the slower growth in Electrical, electronic, and optical products of 0.1 per cent (2022: 11.3%).
此外,森美兰的经济增长了1.8%,由服务业(4.5%)推动,特别是公用事业、交通与仓储以及信息和通信,增幅达5.5%。该州中等经济增长也受到制造业的微弱增长(1.2%)的影响,其中电气、电子和光学产品的增长放缓了0.1%(2022年为11.3%)。
Sabah's economy expanded by 1.3 per cent, driven by a 4.5 per cent growth in the Services sector (2022: 8.5%). The growth was primarily fuelled by the Wholesale & retail trade, food & beverages, and accommodation subsectors, which saw a 4.6 per cent increase.
沙巴的经济增长了1.3%,其中服务业增长了4.5%(2022年为8.5%)。增长主要源于批发和零售贸易、食品和饮料以及住宿子行业,这些板块的增幅达到4.6%。
However, Sabah's Mining & quarrying sector, the state's second highest contributor, contracted by 5.2 per cent, largely due to a 5.7 per cent decline in its main commodities, Crude oil & condensate. Meanwhile, the Agriculture sector, ranking third in its contribution to Sabah's GDP, registered a marginal growth of 0.8 per cent due to 8.9 per cent decrease in the Fisheries subsector.
然而,沙巴的第二大贡献板块矿业和采石业收缩了5.2%,主要归因于主要商品WTI原油和凝结油下降了5.7%。同时,贡献沙巴GDP的第三大板块农业以0.8%的微弱增长,其中渔业子行业下降了8.9%。
Sarawak remains the fourth highest contributor to the country's GDP, registered a 1.2 per cent growth in 2023. The Services sector grew strongly by 5.4 per cent, surpassing the national Services sector's growth rate.
砂拉越仍然是该国GDP的第四大贡献板块,2023年增长了1.2%。服务业增长强劲,增长5.4%,超过全国服务业的增长率。
However, Sarawak's Manufacturing sector, the second highest contributor to its economy, declined by 3.9 per cent. The decline was primarily due to a 4.6 per cent decrease in Petroleum, chemical, rubber, and plastic products, particularly in refined petroleum products. This aligns with the reduction in Crude oil & condensate and Natural gas production of 2.3 per cent and 1.1 per cent respectively, resulting in a 1.0 per cent contraction in Sarawak's Mining & quarrying sector, thus contributing to the slower GDP growth of Sarawak in 2023.
然而,砂拉越的生产制造业——其经济的第二大贡献板块下降了3.9%。下降主要是由于石油、化学、橡胶和塑料制品,特别是精制石油产品下降了4.6%。WTI原油和天然气产量分别下降了2.3%和1.1%,导致砂拉越的矿业和采石业板块收缩了1.0%,从而导致砂拉越2023年的GDP增长放缓。
In terms of GDP per capita, the value of national GDP per capita in 2023 was RM54,612.
根据人均GDP,2023年全国GDP每人为RM54,612。
As for the performance by state, five (5) states recorded GDP per capita values above the national level, namely W.P. Kuala Lumpur (RM131,038), W.P. Labuan (RM83,596), Penang (RM72,586), Sarawak (RM72,411) and Selangor (RM62,492).
至于各州的表现,有五个州的GDP人均值高于全国水平,分别是吉隆坡联邦直辖区(RM131,038)、纳闽联邦直辖区(RM83,596)、槟城(RM72,586)、砂拉越(RM72,411)和雪兰莪(RM62,492)。
DOSM said: "Based on the Leading Index from January to April 2024, Malaysia's economic outlook for 2024 shows continuous growth in the near term. This growth is anticipated as all components are projected to increase, except for Real Imports of Semiconductor.
DOSM表示:“根据2024年1月至4月的领先指标,马来西亚2024年经济前景显示近期持续增长。高达所有板块的指数除半导体实际进口外均有所增长。
Other indicators such as consumer confidence, industrial production, and export flows have demonstrated resilience and growth potential. These factors are expected to contribute to a stable trajectory for the Malaysian economy in the coming year.
其他指标,如消费者信心、工业产量和出口流量均表现出韧性和增长潜力。这些因素预计将有助于马来西亚经济在未来一年中保持稳定的增长轨迹。
Moreover, continued growth is evident in the improved GDP performance in the first quarter of 2024, which recorded a growth rate of 4.2 per cent compared to 2.9 per cent in the previous quarter. This favourable economic environment has also supported stable growth in the national labour market, reflected in an increase in the Labor Force Participation Rate from 70.1 per cent in the fourth quarter of 2023 to 70.2 per cent in the first quarter of 2024.
此外,2024年第一季度的GDP表现改善,与上一季度的2.9%相比,增长率达4.2%。这种有利的经济环境也支持国家劳动力市场的稳定增长,反映在劳动力参与率从2023年第四季度的70.1%上升到2024年第一季度的70.2%。
The Unemployment Rate for the first quarter of 2024 remained steady at 3.3 per cent, consistent with the previous quarter." However, challenges such as global economic uncertainty and commodity price instability continue to be significant factors influencing Malaysia's economic outlook.
2024年第一季度的失业率保持在3.3%,与上一季度持平。然而,全球经济不确定性和商品价格不稳定等挑战仍然是影响马来西亚经济前景的重要因素。
The Department of Statistics Malaysia (DOSM
马来西亚统计局(DOSM
