Is Newmont (NYSE:NEM) Using Too Much Debt?
Is Newmont (NYSE:NEM) Using Too Much Debt?
David Iben put it well when he said, 'Volatility is not a risk we care about. What we care about is avoiding the permanent loss of capital.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. We can see that Newmont Corporation (NYSE:NEM) does use debt in its business. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
大卫·伊本说得好,他说:“波动性不是我们关心的风险。我们关心的是避免资本的永久损失。”当我们思考一家公司的风险有多大时,我们总是喜欢考虑其债务的用途,因为债务过载可能导致破产。我们可以看到,纽蒙特公司(纽约证券交易所代码:NEM)确实在其业务中使用了债务。但更重要的问题是:这笔债务会带来多大的风险?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
为什么债务会带来风险?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more common (but still painful) scenario is that it has to raise new equity capital at a low price, thus permanently diluting shareholders. Of course, debt can be an important tool in businesses, particularly capital heavy businesses. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
一般而言,只有当公司无法通过筹集资金或用自己的现金流轻松还清债务时,债务才会成为真正的问题。最终,如果公司无法履行偿还债务的法律义务,股东可能会一无所获。但是,更常见(但仍然令人痛苦)的情况是,它必须以低廉的价格筹集新的股本,从而永久稀释股东。当然,债务可以成为企业的重要工具,尤其是资本密集型企业。当我们检查债务水平时,我们首先要同时考虑现金和债务水平。
How Much Debt Does Newmont Carry?
纽蒙特背负了多少债务?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at June 2024 Newmont had debt of US$8.69b, up from US$5.57b in one year. However, it also had US$2.65b in cash, and so its net debt is US$6.04b.
您可以点击下图查看更多详情,该图片显示,截至2024年6月,纽蒙特的债务为86.9亿美元,高于一年的55.7亿美元。但是,它也有26.5亿美元的现金,因此其净负债为60.4亿美元。
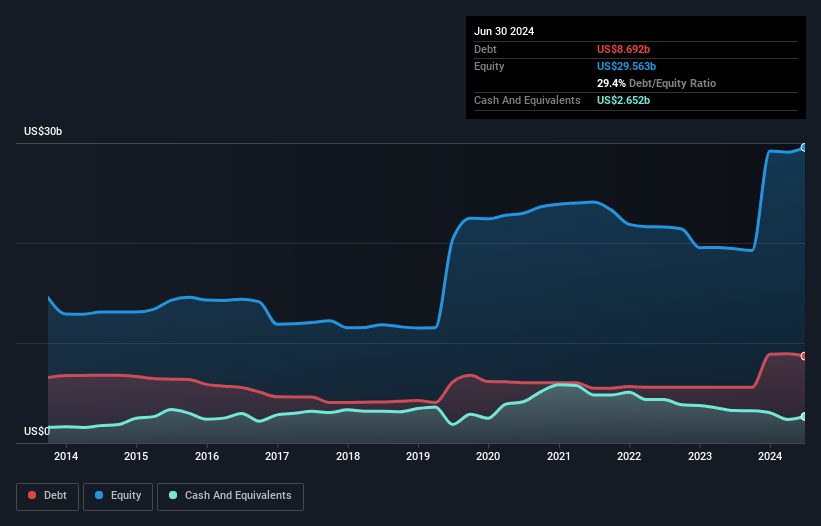
How Strong Is Newmont's Balance Sheet?
纽蒙特的资产负债表有多强?
The latest balance sheet data shows that Newmont had liabilities of US$5.73b due within a year, and liabilities of US$20.4b falling due after that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of US$2.65b as well as receivables valued at US$955.0m due within 12 months. So its liabilities total US$22.5b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
最新的资产负债表数据显示,纽蒙特的负债为57.3亿美元,此后到期的负债为204亿美元。除这些债务外,它有26.5亿美元的现金以及价值9.55亿美元的应收账款将在12个月内到期。因此,其负债总额比其现金和短期应收账款的总和高出225亿美元。
This deficit isn't so bad because Newmont is worth a massive US$54.8b, and thus could probably raise enough capital to shore up its balance sheet, if the need arose. But it's clear that we should definitely closely examine whether it can manage its debt without dilution.
这种赤字还不错,因为纽蒙特的身价高达548亿美元,因此,如果有需要,可能会筹集足够的资金来支撑其资产负债表。但很明显,我们一定要仔细研究它能否在不稀释的情况下管理债务。
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
为了扩大公司相对于收益的负债规模,我们计算其净负债除以利息、税项、折旧和摊销前的收益(EBITDA),将其利息和税前收益(EBIT)除以利息支出(利息保障)。这样,我们既考虑债务的绝对数量,也考虑为债务支付的利率。
Newmont's net debt is only 1.3 times its EBITDA. And its EBIT covers its interest expense a whopping 12.1 times over. So we're pretty relaxed about its super-conservative use of debt. In addition to that, we're happy to report that Newmont has boosted its EBIT by 85%, thus reducing the spectre of future debt repayments. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Newmont can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
纽蒙特的净负债仅为其息税折旧摊销前利润的1.3倍。其息税前利润可支付其高达12.1倍的利息支出。因此,我们对它超保守的债务使用相当放松。除此之外,我们很高兴地报告,纽蒙特已将其息税前利润提高了85%,从而减少了对未来债务偿还的担忧。在分析债务水平时,资产负债表是显而易见的起点。但最终,该业务的未来盈利能力将决定纽蒙特能否随着时间的推移加强其资产负债表。因此,如果您专注于未来,可以查看这份显示分析师利润预测的免费报告。
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Over the most recent three years, Newmont recorded free cash flow worth 72% of its EBIT, which is around normal, given free cash flow excludes interest and tax. This free cash flow puts the company in a good position to pay down debt, when appropriate.
最后,企业需要自由现金流来偿还债务;会计利润根本无法减少债务。因此,值得检查一下该息税前利润中有多少是由自由现金流支持的。在最近三年中,鉴于自由现金流不包括利息和税收,纽蒙特录得的自由现金流占其息税前利润的72%,这几乎是正常的。这种自由现金流使公司处于有利地位,可以在适当的时候偿还债务。
Our View
我们的观点
Happily, Newmont's impressive interest cover implies it has the upper hand on its debt. And the good news does not stop there, as its EBIT growth rate also supports that impression! Looking at the bigger picture, we think Newmont's use of debt seems quite reasonable and we're not concerned about it. While debt does bring risk, when used wisely it can also bring a higher return on equity. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. These risks can be hard to spot. Every company has them, and we've spotted 2 warning signs for Newmont (of which 1 is potentially serious!) you should know about.
令人高兴的是,纽蒙特令人印象深刻的利息保障意味着它在债务上占了上风。好消息不止于此,因为其息税前利润增长率也支持这种印象!从大局来看,我们认为纽蒙特对债务的使用似乎相当合理,我们对此并不担心。虽然债务确实会带来风险,但如果明智地使用,它也可以带来更高的股本回报率。毫无疑问,我们从资产负债表中学到的关于债务的知识最多。但归根结底,每家公司都可以控制资产负债表之外存在的风险。这些风险可能很难发现。每家公司都有警告,我们已经发现了纽蒙特的2个警告信号(其中1个可能很严重!)你应该知道。
If you're interested in investing in businesses that can grow profits without the burden of debt, then check out this free list of growing businesses that have net cash on the balance sheet.
如果你有兴趣投资能够在没有债务负担的情况下增加利润的企业,请查看这份资产负债表上有净现金的成长型企业的免费清单。
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
对这篇文章有反馈吗?对内容感到担忧吗?请直接联系我们。或者,也可以发送电子邮件至编辑团队 (at) simplywallst.com。
Simply Wall St的这篇文章本质上是笼统的。我们仅使用公正的方法根据历史数据和分析师的预测提供评论,我们的文章无意作为财务建议。它不构成买入或卖出任何股票的建议,也没有考虑到您的目标或财务状况。我们的目标是为您提供由基本数据驱动的长期重点分析。请注意,我们的分析可能不考虑最新的价格敏感型公司公告或定性材料。简而言之,华尔街没有持有任何上述股票的头寸。
