ASEAN Power Sector Aims To Achieve 50% RE Capacity By 2040
ASEAN Power Sector Aims To Achieve 50% RE Capacity By 2040

The regional energy collaboration as outlined and coordinated by the ASEAN Plan of Action for Energy Cooperation (APAEC 1999-2025) has identified seven key areas including the latest addition of the civilian nuclear power programme, and is well on the path to achieving 50% renewable energy (RE) power capacity by 2040 in the ASEAN progressive scenario, according to the latest report co-edited by APAEC Drafting Committee (ADC), ASEAN Centre for Energy (ACE), ASEAN Secretariat and ASEAN Specialised Energy Bodies and Sub-sector Networks.
根据东盟能源合作行动计划(APAEC 1999-2025)的概述和协调,区域能源合作已经确定了七个关键领域,包括最近新增的民用核电项目,并且根据由APAEC起草委员会(ADC)、东盟能源中心(ACE)、东盟秘书处以及东盟专业能源机构和子行业网络共同编辑的最新报告,已有望在2040年实现50%的可再生能源(RE)电力产能。
The APAEC 2016-2025 is the fourth and current APAEC extended over a longer period of 10 years. The implementation plan is divided in two (2) phases, namely, Phase I from 2016-2020 and Phase II from 2021-2025.
APAEC 2016-2025是第四个也是当前的APAEC,延长了10年的周期。实施计划分为两个阶段,即第一阶段从2016年到2020年,第二阶段从2021年到2025年。
The APAEC Phase I 2016-2020 focused on the short- to medium-term strategies to achieve energy security, accessibility, affordability and sustainability for All. Meanwhile, the APAEC Phase II 2021-2025 is the continuation of Phase I with higher aspirational targets and new initiatives to enhance energy transition and resilience towards a sustainable future. Notably, the Phase II takes into account the impact of COVID-19 pandemic and its recovery plans, recent global economic and energy trends, cross-cutting issues such as climate change and
decarbonisation, energy investment and financing projects, inclusion of private sectors through business forum activities, new and emerging energy technologies, and digitalisation in the energy sector.
APAEC第一阶段2016-2020的重点是实现所有板块的能源安全、可及性、可负担性和可持续性的短期和中期战略。与此同时,APAEC第二阶段2021-2025是第一阶段的延续,设定了更高的目标和新的倡议,以增强能源转型和韧性,迈向可持续的未来。值得注意的是,第二阶段考虑到了COVID-19大流行的影响及其恢复计划,最近的全球经济和能源趋势、气候变化等横向问题,以及
减碳、能源投资和融资项目、通过商业论坛活动纳入私营部门、新兴的能源科技,以及能源领域的数字化。
Concerning RE goals and objectives, the results will be viewed in two perspectives namely the ASEAN APAEC progressive scenario (APS) and the ASEAN member states target scenario (ATS). The APS assumes that regional targets as per the APAEC 2016-2025 are reached. On the other hand, the ATS assumes that the most recent renewable energy and energy efficiency targets of member states are reached.
关于可再生能源(RE)目标和指标,结果将从两个角度来看,即东盟APAEC进步情景(APS)和东盟成员国目标情景(ATS)。APS假设按照APAEC 2016-2025的区域目标达成。另一方面,ATS假设达成成员国最近的可再生能源和能效目标。
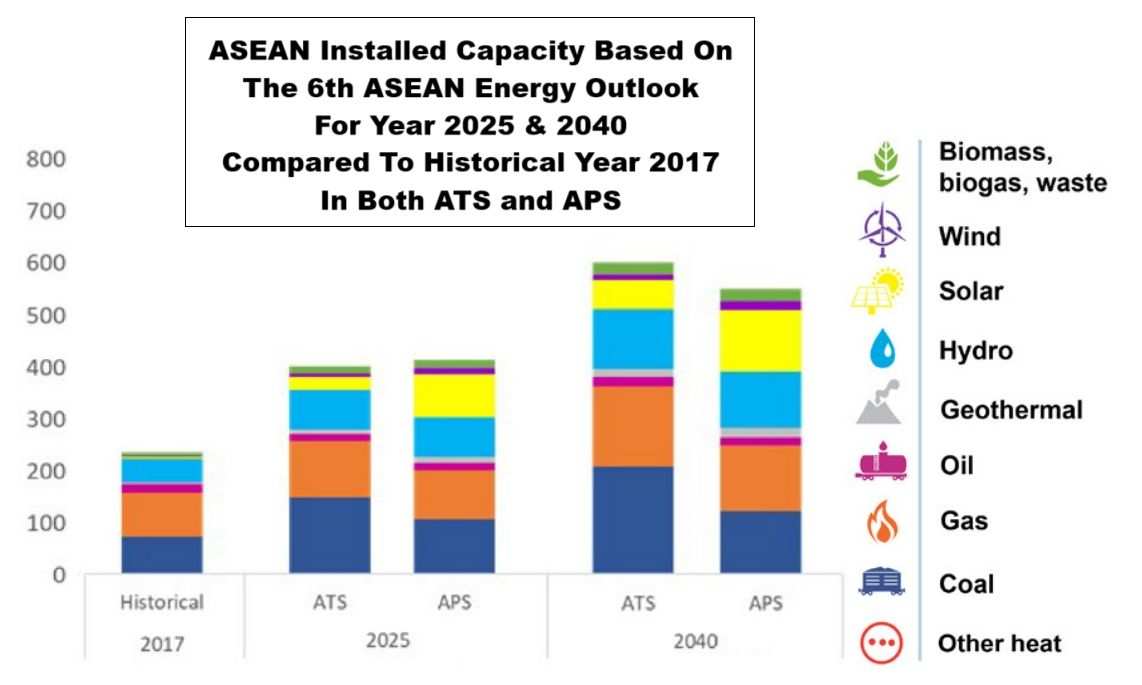
According to a graphical presentation embedded in the report, the power sector plays a significant role in stimulating the share of renewable energy (RE) in the region, including biomass, wind, solar, geothermal, and hydro power. By 2025, the share of RE in installed power capacity will be 33% in the ATS and 48% in the APS. The RE share in installed capacity is dominated by hydro, followed by solar power in the ATS. Solar will more than triple its installed capacity in the APS, and the shares in installed capacity will increase to nearly 20% of total capacity.
根据报告中嵌入的图形展示,电力产业在刺激区域内可再生能源(RE)比例方面发挥了重要作用,包括生物质、风能、太阳能、地热能和水电。到2025年,可再生能源在已安装电力容量中的份额将在ATS中为33%,在APS中为48%。已安装容量中的可再生能源份额以水电为主,其次是ATS中的太阳能。在APS中,太阳能的已安装容量将增加到原来的三倍以上,其已安装容量的份额将接近总容量的20%。
By 2040, the share of RE in installed capacity will surpass one-third of the total capacity in ATS and will account for almost 50% of the total power capacity in APS. In ATS, RE capacity is led by hydro but hydro and solar are nearly at par in APS.
到2040年,已装机容量中可再生能源所占比例将超过ATS总容量的三分之一,并将占APS总电力容量的近50%。在ATS中,可再生能源容量以水力为主,但在APS中水力与太阳能几乎持平。
Meanwhile, the seven key areas of energy collaboration include regional power grid for electricity trading, region-wide gas pipeline to develop a common gas market, regional energy policy and planning to accelerate transition, clean coal technology to lower carbon emission, energy efficiency and conservation especially in transport and industry sectors, increased renewable energy capacity to 23% by 2025, and lastly, civilian nuclear energy (CNE) for power generation, which is the latest key area added during the third APAEC 2010-2015 to facilitate information exchange and capacity building in nuclear energy.
与此同时,能源合作的七个关键领域包括,区域电网用于电力交易,区域范围内的天然气管道以发展共同的天然气市场,区域能源政策与规划以加速转型,清洁煤技术以降低碳排放,特别是在交通和行业板块的能源效率与节能,到2025年将可再生能源容量提高到23%,最后是用于发电的民用核能(CNE),这是在第三个APAEC 2010-2015期间新增的关键领域,以促进核能的信息交流和能力建设。
According to a Bernama report dated Dec 21, the Malaysian Nuclear Agency (Nuklear Malaysia) is ready to join other ASEAN member states to advance nuclear research and development (R&D) and nuclear safety in the region as Malaysia assumes the ASEAN Chairmanship in 2025.
根据12月21日的伯纳马报道,马来西亚核能机构(核能马来西亚)已准备好与其他东盟成员国共同推进核研究与开发(R&D)及区域内的核安全,因马来西亚将在2025年担任东盟主席国。
Director General of the agency Dr Rosli Darmawan said Malaysia will play host to the 8th Annual Conference of ASEAN Network on Nuclear Power Safety Research for the first time since its first meeting held in 2017. He added that the 2025 meeting will discuss the achievement and implementation of programmes, in addition to identifying the energy needs of member states.
该机构的总干事罗斯里·达尔马万博士表示,马来西亚将首次主办东盟核电安全研究网络第八届年会,该会议自2017年第一次会议以来首次举行。他补充说,2025年的会议将讨论项目的成就与实施,并确定成员国的能源需求。

 Concerning RE goals and objectives, the results will be viewed in two perspectives namely the ASEAN APAEC progressive scenario (APS) and the ASEAN member states target scenario (ATS). The APS assumes that regional targets as per the APAEC 2016-2025 are reached. On the other hand, the ATS assumes that the most recent renewable energy and energy efficiency targets of member states are reached.
Concerning RE goals and objectives, the results will be viewed in two perspectives namely the ASEAN APAEC progressive scenario (APS) and the ASEAN member states target scenario (ATS). The APS assumes that regional targets as per the APAEC 2016-2025 are reached. On the other hand, the ATS assumes that the most recent renewable energy and energy efficiency targets of member states are reached.