RTX (NYSE:RTX) Has A Pretty Healthy Balance Sheet
RTX (NYSE:RTX) Has A Pretty Healthy Balance Sheet
David Iben put it well when he said, 'Volatility is not a risk we care about. What we care about is avoiding the permanent loss of capital.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We can see that RTX Corporation (NYSE:RTX) does use debt in its business. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
大卫·伊本很恰当地说,'波动性不是我们关心的风险。我们关心的是避免资本的永久损失。' 所以当你考虑任何给定股票的风险时,考虑债务可能是显而易见的,因为过多的债务可能会让公司陷入困境。我们可以看到RTX公司(纽交所:RTX)确实在其业务中使用债务。但是,更重要的问题是:这些债务创造了多少风险?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
债务何时会变得危险?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Having said that, the most common situation is where a company manages its debt reasonably well - and to its own advantage. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
一般来说,债务只有在公司无法轻松偿还时才会成为真正的问题,无论是通过筹集资金还是通过自身的现金流。在最坏的情况下,如果一家公司无法偿还其债权人,它可能会破产。然而,更常见(但仍然昂贵)的情况是,公司必须在低廉的股票价格下稀释股东权益,仅仅是为了控制债务。话虽如此,最常见的情况是公司合理管理其债务,并使之对自身有利。当我们检查债务水平时,我们首先考虑现金和债务水平的结合。
What Is RTX's Debt?
RTX的债务是多少?
As you can see below, at the end of September 2024, RTX had US$42.1b of debt, up from US$35.2b a year ago. Click the image for more detail. On the flip side, it has US$6.68b in cash leading to net debt of about US$35.4b.
正如您在下面看到的,到2024年9月底,RTX的债务为421亿美元,较一年前的352亿美元有所上升。点击图片获取更多详情。另一方面,它的现金为66.8亿美元,导致净债务约为354亿美元。
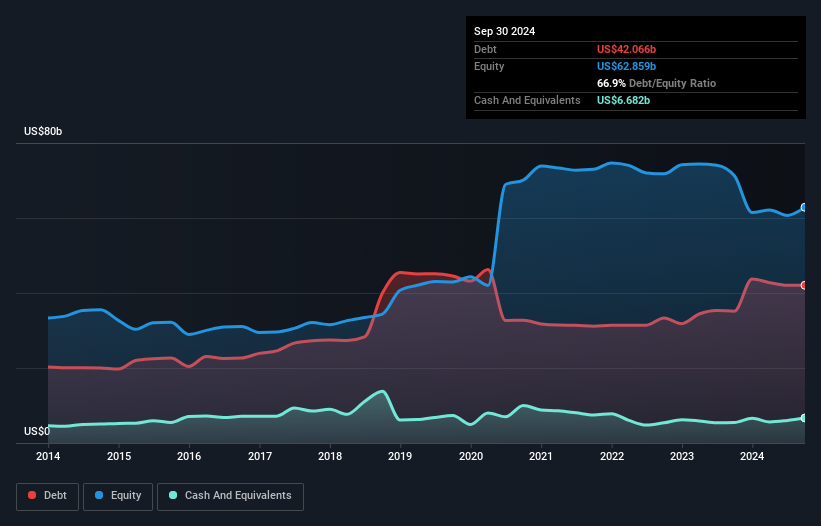
How Strong Is RTX's Balance Sheet?
RTX的资产负债表有多强?
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that RTX had liabilities of US$52.2b due within 12 months and liabilities of US$49.7b due beyond that. Offsetting this, it had US$6.68b in cash and US$24.8b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling US$70.5b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
仔细查看最新的资产负债表数据,我们可以看到RTX有522亿美元的负债将在12个月内到期,以及497亿美元的负债将在此之后到期。 另一方面,它有66.8亿美元的现金和248亿美元的应收账款将在12个月内到期。因此,它的负债总额比现金和短期应收款加起来多出705亿美元。
This deficit isn't so bad because RTX is worth a massive US$155.5b, and thus could probably raise enough capital to shore up its balance sheet, if the need arose. But we definitely want to keep our eyes open to indications that its debt is bringing too much risk.
这个赤字并不算太糟糕,因为RTX的市值高达1555亿美元,因此如果需要的话,可能能够筹集足够的资本来增强其资产负债表。但我们确实想要保持警惕,以观察其债务是否带来了过多的风险。
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
为了评估一家公司的债务相对于其收益的情况,我们计算其净债务与息税折旧摊销前利润(EBITDA)的比率,以及息税利润(EBIT)与利息费用(即利息覆盖)的比率。这种方法的优点在于我们同时考虑到债务的绝对数额(使用净债务与EBITDA的比率)和与该债务相关的实际利息支出(使用利息覆盖率)。
RTX's debt is 2.8 times its EBITDA, and its EBIT cover its interest expense 4.4 times over. This suggests that while the debt levels are significant, we'd stop short of calling them problematic. The good news is that RTX grew its EBIT a smooth 56% over the last twelve months. Like the milk of human kindness that sort of growth increases resilience, making the company more capable of managing debt. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine RTX's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
RTX的债务是其EBITDA的2.8倍,其EBIT覆盖利息费用4.4倍。这表明尽管债务水平很高,但我们仍然不会称其为有问题。好消息是RTX在过去12个月中,EBIT增长了平稳的56%。像人类善良的牛奶一样,这种增长提高了弹性,使公司更有能力管理债务。在分析债务水平时,资产负债表显然是一个好的起点。但未来的收益比任何其他因素更能判断RTX未来保持健康资产负债表的能力。因此,如果你想知道专业人士的看法,可能会发现这份关于分析师利润预测的免费报告很有趣。
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. During the last three years, RTX produced sturdy free cash flow equating to 72% of its EBIT, about what we'd expect. This free cash flow puts the company in a good position to pay down debt, when appropriate.
最后,一家公司只能用冷硬的现金偿还债务,而不是会计利润。所以逻辑步骤是查看EBIT中实际自由现金流的比例。在过去三年中,RTX产生了相当于其EBIT的72%的强劲自由现金流,差不多是我们所期望的。这种自由现金流让公司在适当的时候能够偿还债务。
Our View
我们的观点
The good news is that RTX's demonstrated ability to grow its EBIT delights us like a fluffy puppy does a toddler. But truth be told we feel its net debt to EBITDA does undermine this impression a bit. All these things considered, it appears that RTX can comfortably handle its current debt levels. On the plus side, this leverage can boost shareholder returns, but the potential downside is more risk of loss, so it's worth monitoring the balance sheet. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. Be aware that RTX is showing 2 warning signs in our investment analysis , you should know about...
好消息是RTX显示出增长其EBIT的能力,像毛茸茸的小狗让幼儿快乐一样让我们欣喜。但说实话,我们觉得其净债务与EBITDA的比率确实有些削弱了这种印象。考虑到所有这些,RTX似乎可以轻松应对目前的债务水平。积极的一面是,这种杠杆可以提升股东回报,但潜在的 downside 是损失风险增加,因此值得关注资产负债表。资产负债表显然是分析债务时要关注的重点。然而,并非所有投资风险都存在于资产负债表中,远非如此。请注意,RTX在我们的投资分析中显示出两个警告信号,你应该知道...
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
最终,通常更好的是关注没有净负债的公司。你可以访问我们特别列出这些公司的名单(所有公司都有盈利增长的记录)。这是免费的。
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
对本文有反馈?对内容有疑虑?请直接与我们联系。或者,发送电子邮件至 editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com。
这篇来自Simply Wall St的文章是一般性的。我们根据历史数据和分析师预测提供评论,采用无偏见的方法,我们的文章并不旨在提供财务建议。它不构成对任何股票的买入或卖出建议,也未考虑到您的目标或财务状况。我们旨在为您提供以基本数据驱动的长期分析。请注意,我们的分析可能未考虑最新的价格敏感公司公告或定性材料。Simply Wall St在提到的任何股票中均没有持仓。

 Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that RTX had liabilities of US$52.2b due within 12 months and liabilities of US$49.7b due beyond that. Offsetting this, it had US$6.68b in cash and US$24.8b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling US$70.5b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that RTX had liabilities of US$52.2b due within 12 months and liabilities of US$49.7b due beyond that. Offsetting this, it had US$6.68b in cash and US$24.8b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling US$70.5b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.