Is Kraft Heinz (NASDAQ:KHC) A Risky Investment?
Is Kraft Heinz (NASDAQ:KHC) A Risky Investment?
Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We note that The Kraft Heinz Company (NASDAQ:KHC) does have debt on its balance sheet. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. Part and parcel of capitalism is the process of 'creative destruction' where failed businesses are mercilessly liquidated by their bankers. While that is not too common, we often do see indebted companies permanently diluting shareholders because lenders force them to raise capital at a distressed price. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
What Is Kraft Heinz's Debt?
The chart below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that Kraft Heinz had US$20.5b in debt in March 2024; about the same as the year before. However, it does have US$1.63b in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about US$18.9b.
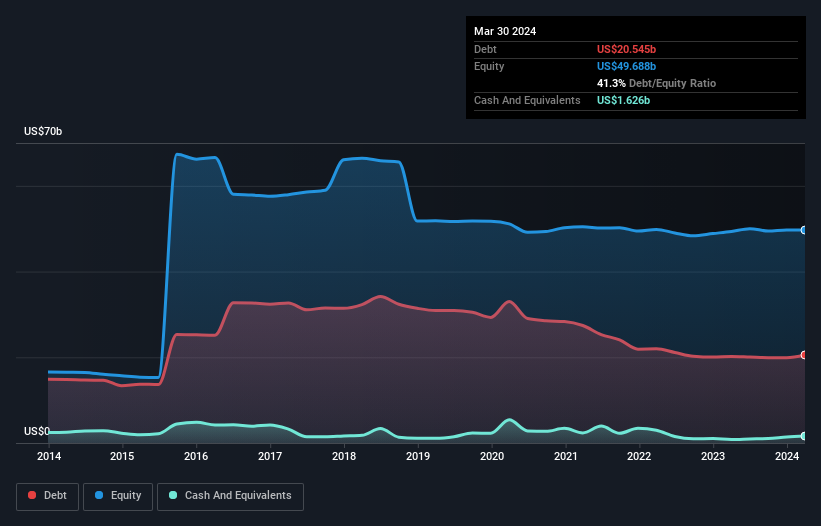
How Strong Is Kraft Heinz's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Kraft Heinz had liabilities of US$7.57b due within 12 months, and liabilities of US$33.1b due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of US$1.63b as well as receivables valued at US$2.22b due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling US$36.8b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
This is a mountain of leverage even relative to its gargantuan market capitalization of US$40.5b. Should its lenders demand that it shore up the balance sheet, shareholders would likely face severe dilution.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
Kraft Heinz's debt is 2.9 times its EBITDA, and its EBIT cover its interest expense 6.4 times over. This suggests that while the debt levels are significant, we'd stop short of calling them problematic. We saw Kraft Heinz grow its EBIT by 7.9% in the last twelve months. Whilst that hardly knocks our socks off it is a positive when it comes to debt. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Kraft Heinz can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. During the last three years, Kraft Heinz produced sturdy free cash flow equating to 56% of its EBIT, about what we'd expect. This cold hard cash means it can reduce its debt when it wants to.
Our View
Both Kraft Heinz's level of total liabilities and its net debt to EBITDA were discouraging. But its not so bad at converting EBIT to free cash flow. We think that Kraft Heinz's debt does make it a bit risky, after considering the aforementioned data points together. That's not necessarily a bad thing, since leverage can boost returns on equity, but it is something to be aware of. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. To that end, you should be aware of the 2 warning signs we've spotted with Kraft Heinz .
If, after all that, you're more interested in a fast growing company with a rock-solid balance sheet, then check out our list of net cash growth stocks without delay.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com
