David Iben put it well when he said, 'Volatility is not a risk we care about. What we care about is avoiding the permanent loss of capital.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. We note that Anhui Expressway Company Limited (HKG:995) does have debt on its balance sheet. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
What Is Anhui Expressway's Net Debt?
As you can see below, Anhui Expressway had CN¥6.98b of debt, at March 2024, which is about the same as the year before. You can click the chart for greater detail. However, it does have CN¥4.77b in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about CN¥2.20b.
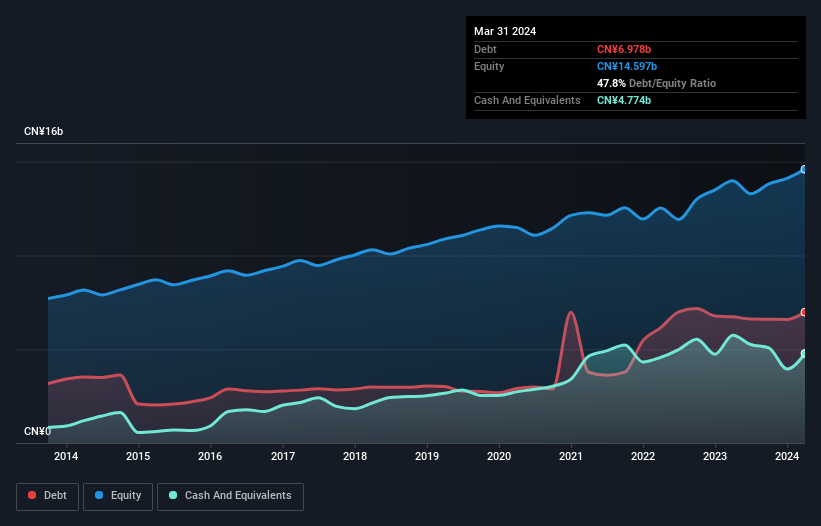
A Look At Anhui Expressway's Liabilities
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that Anhui Expressway had liabilities of CN¥1.52b due within 12 months and liabilities of CN¥6.53b due beyond that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of CN¥4.77b as well as receivables valued at CN¥131.9m due within 12 months. So its liabilities total CN¥3.14b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
Of course, Anhui Expressway has a market capitalization of CN¥19.5b, so these liabilities are probably manageable. Having said that, it's clear that we should continue to monitor its balance sheet, lest it change for the worse.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Anhui Expressway's net debt is only 0.68 times its EBITDA. And its EBIT covers its interest expense a whopping 74.4 times over. So you could argue it is no more threatened by its debt than an elephant is by a mouse. The good news is that Anhui Expressway has increased its EBIT by 7.4% over twelve months, which should ease any concerns about debt repayment. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Anhui Expressway can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, while the tax-man may adore accounting profits, lenders only accept cold hard cash. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. Looking at the most recent three years, Anhui Expressway recorded free cash flow of 43% of its EBIT, which is weaker than we'd expect. That's not great, when it comes to paying down debt.
Our View
The good news is that Anhui Expressway's demonstrated ability to cover its interest expense with its EBIT delights us like a fluffy puppy does a toddler. And the good news does not stop there, as its net debt to EBITDA also supports that impression! We would also note that Infrastructure industry companies like Anhui Expressway commonly do use debt without problems. Taking all this data into account, it seems to us that Anhui Expressway takes a pretty sensible approach to debt. While that brings some risk, it can also enhance returns for shareholders. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. For instance, we've identified 1 warning sign for Anhui Expressway that you should be aware of.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com

