Some say volatility, rather than debt, is the best way to think about risk as an investor, but Warren Buffett famously said that 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. We note that Ball Corporation (NYSE:BALL) does have debt on its balance sheet. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. While that is not too common, we often do see indebted companies permanently diluting shareholders because lenders force them to raise capital at a distressed price. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
What Is Ball's Net Debt?
As you can see below, Ball had US$5.79b of debt at June 2024, down from US$9.74b a year prior. On the flip side, it has US$1.36b in cash leading to net debt of about US$4.43b.
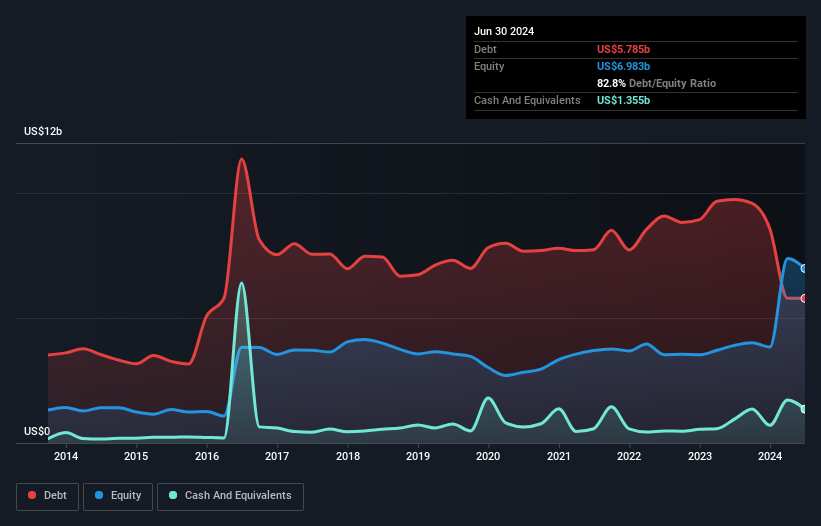
How Strong Is Ball's Balance Sheet?
 The latest balance sheet data shows that Ball had liabilities of US$4.89b due within a year, and liabilities of US$7.09b falling due after that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of US$1.36b as well as receivables valued at US$2.71b due within 12 months. So its liabilities total US$7.91b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
The latest balance sheet data shows that Ball had liabilities of US$4.89b due within a year, and liabilities of US$7.09b falling due after that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of US$1.36b as well as receivables valued at US$2.71b due within 12 months. So its liabilities total US$7.91b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
Ball has a very large market capitalization of US$19.3b, so it could very likely raise cash to ameliorate its balance sheet, if the need arose. But we definitely want to keep our eyes open to indications that its debt is bringing too much risk.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Ball's net debt is sitting at a very reasonable 2.1 times its EBITDA, while its EBIT covered its interest expense just 3.9 times last year. While that doesn't worry us too much, it does suggest the interest payments are somewhat of a burden. We note that Ball grew its EBIT by 23% in the last year, and that should make it easier to pay down debt, going forward. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Ball can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, while the tax-man may adore accounting profits, lenders only accept cold hard cash. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. During the last three years, Ball burned a lot of cash. While investors are no doubt expecting a reversal of that situation in due course, it clearly does mean its use of debt is more risky.
Our View
Ball's struggle to convert EBIT to free cash flow had us second guessing its balance sheet strength, but the other data-points we considered were relatively redeeming. In particular, its EBIT growth rate was re-invigorating. Taking the abovementioned factors together we do think Ball's debt poses some risks to the business. While that debt can boost returns, we think the company has enough leverage now. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. For example, we've discovered 3 warning signs for Ball (2 are a bit unpleasant!) that you should be aware of before investing here.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.

