Summary
The Institute for Supply Management published its monthly Manufacturing Report for October.The latest headline Purchasing Managers Index was 48.3, an increase of 0.5 percent from 47.8 the previous month.For a diffusion index, the latest reading of 48.3 is its second consecutive month of contraction. By Jill Mislinski
By Jill Mislinski
Today, the Institute for Supply Management published its monthly Manufacturing Report for October. The latest headline Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) was 48.3, an increase of 0.5 percent from 47.8 the previous month. Today's headline number was below the Investing.com forecast of 48.9 percent.
Here is the key analysis from the report:
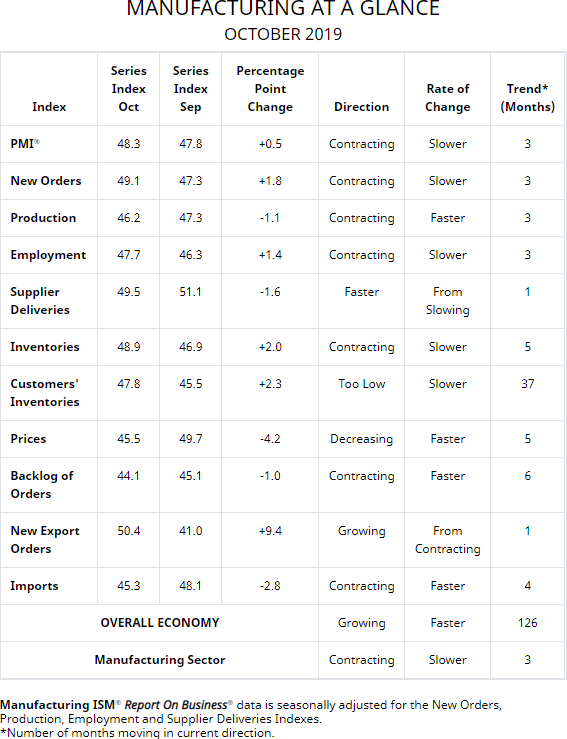
"The October PMI registered 48.3 percent, an increase of 0.5 percentage point from the September reading of 47.8 percent. The New Orders Index registered 49.1 percent, an increase of 1.8 percentage points from the September reading of 47.3 percent. The Production Index registered 46.2 percent, down 1.1 percentage points compared to the September reading of 47.3 percent. The Backlog of Orders Index registered 44.1 percent, down 1 percentage point compared to the September reading of 45.1 percent. The Employment Index registered 47.7 percent, a 1.4-percentage point increase from the September reading of 46.3 percent. The Supplier Deliveries Index registered 49.5 percent, a 1.6-percentage point decrease from the September reading of 51.1 percent. The Inventories Index registered 48.9 percent, an increase of 2 percentage points from the September reading of 46.9 percent. The Prices Index registered 45.5 percent, a 4.2-percentage point decrease from the September reading of 49.7 percent. The New Export Orders Index registered 50.4 percent, a 9.4-percentage point increase from the September reading of 41 percent. The Imports Index registered 45.3 percent, a 2.8-percentage point decrease from the September reading of 48.1 percent.
Here is the table of PMI components.
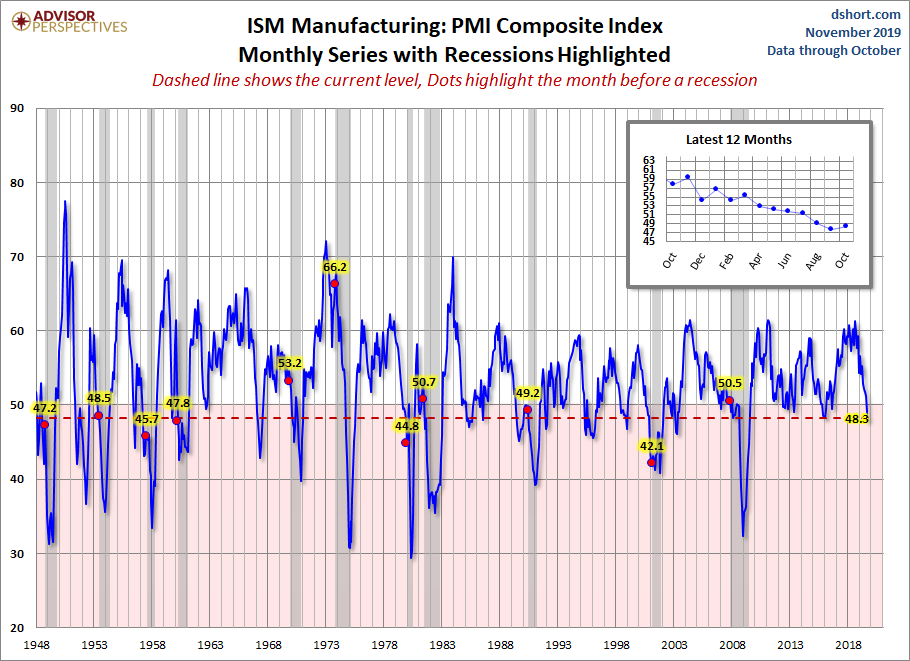
The chart below shows the Manufacturing Composite series, which stretches back to 1948. The eleven recessions during this time frame are indicated along with the index value the month before the recession starts.
For a diffusion index, the latest reading of 48.3 is its second consecutive month of contraction. What sort of correlation does that have with the months before the start of recessions? Check out the red dots in the chart above.
Here is a closer look at the series beginning at the turn of the century.
Note: This commentary used the FRED USRECP series (Peak through the Period preceding the Trough) to highlight the recessions in the charts above. For example, the NBER dates the last cycle peak as December 2007, the trough as June 2009 and the duration as 18 months. The USRECP series thus flags December 2007 as the start of the recession and May 2009 as the last month of the recession, giving us the 18-month duration. The dot for the last recession in the charts above is thus for November 2007. The "Peak through the Period preceding the Trough" series is the one FRED uses in its monthly charts, as illustrated here.
Editor's Note: The summary bullets for this article were chosen by Seeking Alpha editors.