[July.2024] Decoding the Earnings of TSMC, the World's Top Chipmaker
The semiconductor industry is often regarded as the crown jewel of modern technology. Among its key players is TSMC, or Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, which boasts the most advanced chip foundries in the world. As such, the company's financial health mirrors the cyclical nature of the chip market, with considerable swings in its stock price over the past few years.
Since May, TSMC's stock has hit new highs, nearing a trillion-dollar market cap. This surge is partly fueled by Apple's price cuts boosting high-end smartphone chip demand and the ongoing strong demand from data centers.
 Each time a company releases its financial report, it may present a potential trading or investment opportunity. But before diving in, investors need to understand how to interpret their financial statements.
Each time a company releases its financial report, it may present a potential trading or investment opportunity. But before diving in, investors need to understand how to interpret their financial statements.
How do we analyze TSMC's earnings reports, and how can we pinpoint its current phase in the business cycle? Key indicators to watch may include revenue growth and gross margin, the composition of its income, capital expenditures, and cash flow.
1. Revenue growth and gross margin
For cyclical industries, shifts in revenue growth and profit margins are key indicators of the cycle's direction. High growth in revenue and improving gross margins usually signal a peak in the cycle, while the opposite could suggest a downturn.
TSMC's revenue, after three-quarters of sequential declines, showed signs of recovery in the third quarter of 2023 with a 10.2% increase, followed by a 14.4% increase in the fourth quarter.
By Q1 2024, TSMC reported revenue of NT$592.64 billion, marking a 5.3% decline from the previous quarter, halting its rebound trend. However, compared to the same period last year, TSMC's revenue still saw a growth of approximately 16.5%.
TSMC's revenue is determined by the product of shipment volumes and prices, both of which saw a rise in Q4 2023, indicating a possible rebound in demand.
TSMC calculates its revenue by multiplying product shipment volumes by their prices. In Q1 2024, the company's revenue declined quarter-over-quarter primarily due to a drop in product prices. This was largely driven by a significant decrease in Apple smartphone sales, which in turn reduced demand for TSMC's highest-priced 3nm chip manufacturing services, leading to an overall decline in prices.
However, Apple's aggressive price cuts in the second quarter have sparked a strong rebound in its sales. Additionally, Apple's upcoming new models, which will feature integrated AI capabilities, have heightened market expectations for the new generation's sales. This may potentially raise TSMC's average selling prices, thereby boosting future revenue growth.
Regarding gross margin, TSMC reported approximately 53.1% in Q1 2024, still at a relatively low level, possibly due to the high costs of ramping up 3nm chip production.
Although TSMC's revenue has increased for two consecutive quarters—hinting at a warming industry demand—the gross margin has not yet shown a definitive recovery, likely because the demand surge isn't strong enough to boost profitability. Close monitoring of revenue and gross margin trends will be essential to gauge the cycle's rebound.
Overall, TSMC's revenue growth has shown signs of improvement, suggesting a potential recovery in industry demand. However, the growth rate remains somewhat unstable. TSMC's gross profit margin is still relatively low, partly due to high depreciation costs, but more importantly because the demand surge has not been strong enough to boost profitability.
Moving forward, we may continue to monitor TSMC's revenue and gross profit margin trends to better determine the stability and extent of its cyclical recovery.
2. Revenue mix
TSMC's revenue mix is primarily comprised of sales from the smartphone and high-performance computing sectors, which collectively make up about 80% of its total revenue.
During the fourth quarter of 2023, the company witnessed a notable increase in smartphone-related revenue, which rose from a 33% share in the second quarter to 43% by Q4. This significant increase suggests a rebound in the global smartphone market demand.
However, in Q1 2024, the decline in Apple smartphone sales led to a decrease in TSMC's revenue share from the smartphone segment. Conversely, driven by strong demand from data centers and AI, TSMC's high-performance computing segment saw its revenue contribution to TSMC reach a new high in recent quarters.
Moving forward, we may continue to monitor the cyclical changes in smartphone market demand and the sustained robustness of data center demand. These factors will significantly impact TSMC's overall performance.
In terms of chip manufacturing technology, TSMC categorizes its revenue into two segments: advanced sub-7nm processes and the less advanced 7nm-and-above processes. The sub-7nm category, which includes the latest and more sophisticated technology, is where TSMC earns the majority of its income.
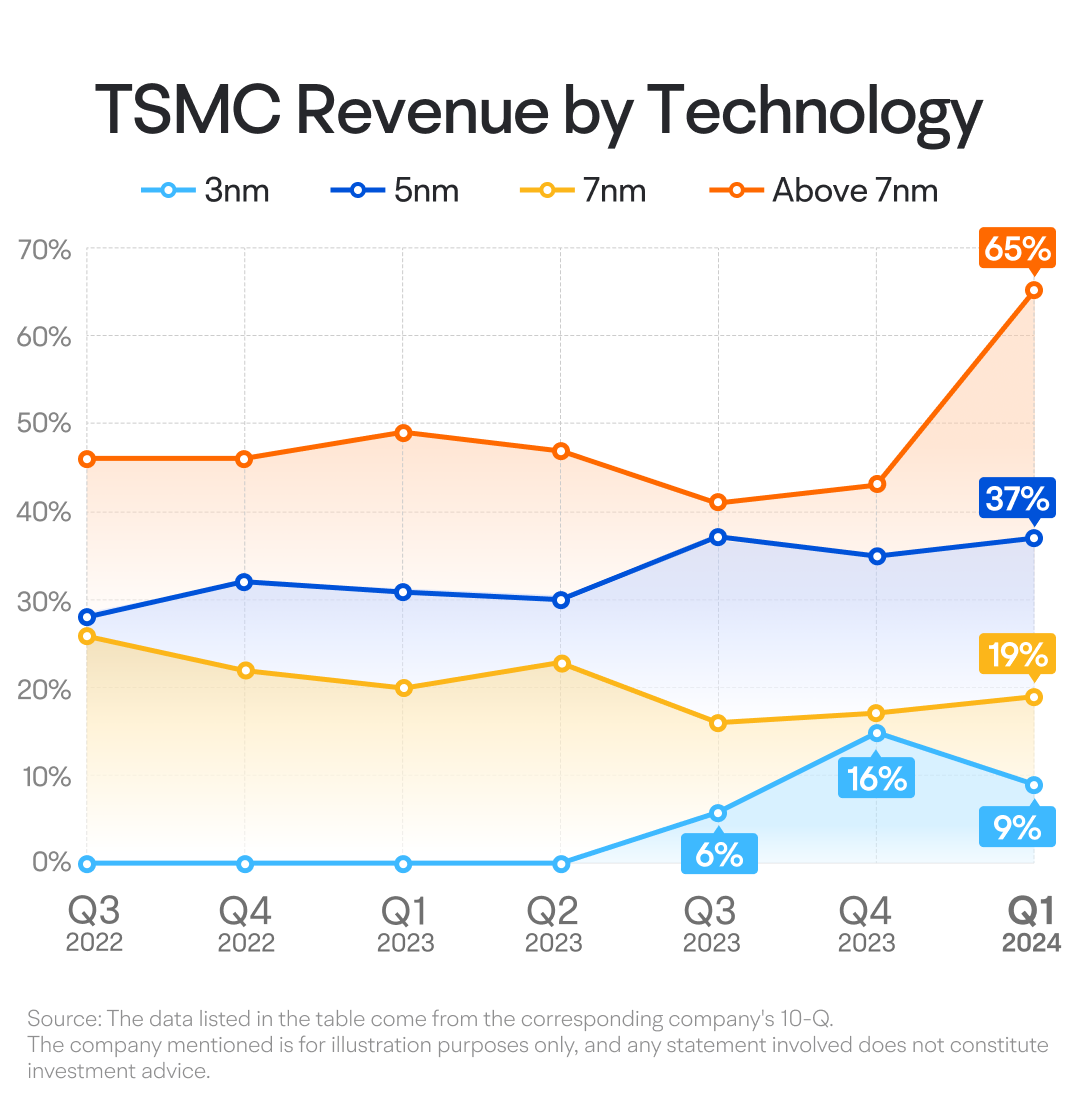
Historically, TSMC's sub-7nm revenues were dominated by 5nm and 7nm process chips, but there has been a shift towards the even more advanced 5nm process. In the third quarter of 2023, TSMC began mass-producing chips using the 3nm process technology, contributing approximately 6% to the overall revenue, with this figure climbing to 15% in the fourth quarter. However, in Q1 2024, Apple's sales declined, reducing TSMC's revenue share from the smartphone segment to 9%.
In the coming quarters, the anticipated sales growth from Apple's price cuts and strong expectations for new models, along with the launch of the latest high-end Android devices, may potentially boost TSMC's revenue from its 3nm technology segment. This increase in demand may drive overall revenue growth for the company.
As we look to the future, the success of TSMC's 3nm technology is expected to grow further, especially with the anticipated launches of new Apple devices and the latest high-end Android smartphones. These product releases are likely to drive an increase in TSMC's 3nm process revenue, further boosting the company's growth.
3. Capital expenditure and cash flow
As the leading semiconductor foundry and second only to NVIDIA in market value within the chip industry, TSMC occupies a prestigious but challenging position. The company must continuously innovate to stay ahead, as the industry relentlessly pushes for more advanced technologies, spurred by Moore's Law. If TSMC were to fall behind, competitors like Samsung Electronics could quickly surpass it.
TSMC's commitment to innovation has led to high capital expenditures. From 2006 to 2023, its cumulative capital spending totaled 6.7 trillion New Taiwan Dollars, even exceeding its net income of 6 trillion during that period. This investment strategy resulted in a cumulative free cash flow of approximately 3.3 trillion, just 60% of its net income.
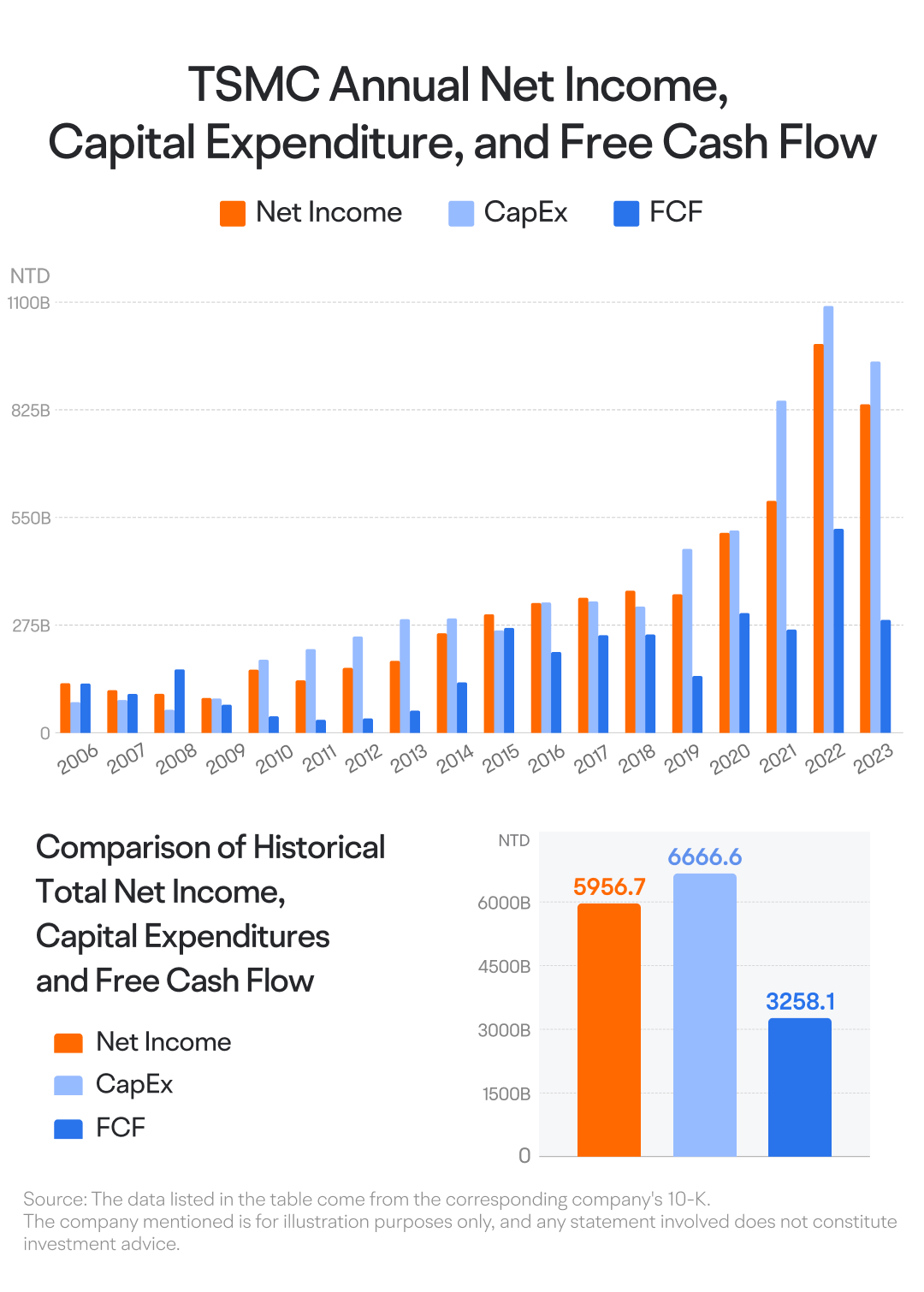
Since free cash flow is a key valuation indicator, this discrepancy could negatively affect TSMC's valuation and long-term stock price.
In the short term, TSMC's capital expenditure reflects its outlook on industry cycles. Typically, if a company predicts a downturn, it may cut back on capital spending, whereas a sustained upturn might lead to increased expenditures. Recent quarters have seen TSMC reduce its capital spending. However, in Q1 2024, TSMC's capital expenditure saw a rebound, and it will be important to monitor these expenditures moving forward.
In the long run, however, TSMC's expenditure trends may align with the technological trends in wafer manufacturing. If Moore's Law eventually becomes obsolete and chip process technology reaches a plateau, TSMC's growth in capital expenditures may also slow down. At that point, with competitors possibly catching up and increasing competitive pressure, TSMC might improve its cash flow but face potential declines in gross margins, which could present a new set of competitive and valuation challenges.
Having read this far, you may now have a deeper understanding of how to interpret TSMC's financial reports. It's noteworthy that the release of earnings reports from prominent companies may present unique trading opportunities for different types of investors.
For instance, if an investor, after analyzing past reports and considering recent developments, believes a company's latest earnings will send positive signals and boost the short-term stock price, they might consider taking a long position. This could involve buying the underlying stock or purchasing call options.
Conversely, if the investor expects the earnings to be unfavorable and potentially pressure the stock price, they might consider taking a short position, either through short selling or buying put options.
If the report's outcome is unclear but volatility is expected, they might use a straddle strategy, buying both calls and puts.
However, investors should carefully assess their risk tolerance, particularly when considering high-risk trades like short selling or options, before making any trading decisions.
In summary
TSMC has seen a sequential rebound in revenue for two consecutive quarters, while their gross margin continued a downward trend. Signs of a cyclical recovery warrant further observation.
Regarding revenue composition, a warming smartphone market could positively influence TSMC's sales. Additionally, the mass production of TSMC's 3nm technology may further drive revenue growth.
TSMC's significant capital expenditures have a substantial impact on its free cash flow and, consequently, its valuation. Capital expenditures should be monitored from both short-term and long-term perspectives.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational and educational purposes only and does not constitute a recommendation or endorsement of any specific investment or investment strategy.
