According to the Daily Economic News, a major bank will reduce its deposit benchmark interest rate on July 25, with a 20 basis point reduction for a 2-year term. More news is being updated.
On Thursday, July 25th Beijing time, according to the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China's (ICBC) website, ICBC lowered its deposit lending rates. It is worth noting that the lending rate is the interest rate on deposits that banks publish on their official websites and the actual rates may not be the same as the lending rates.
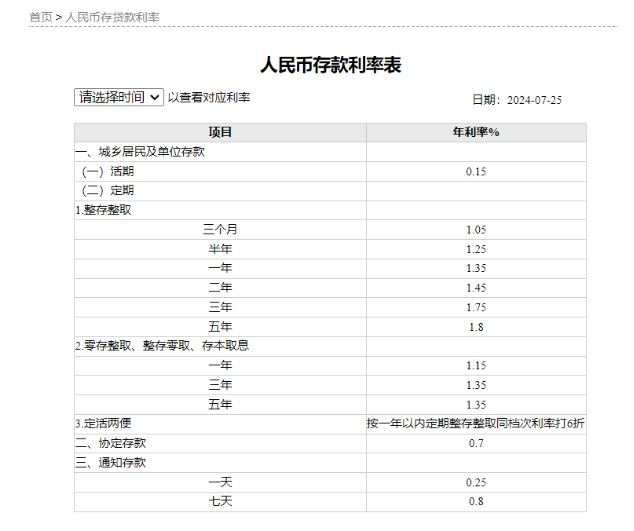
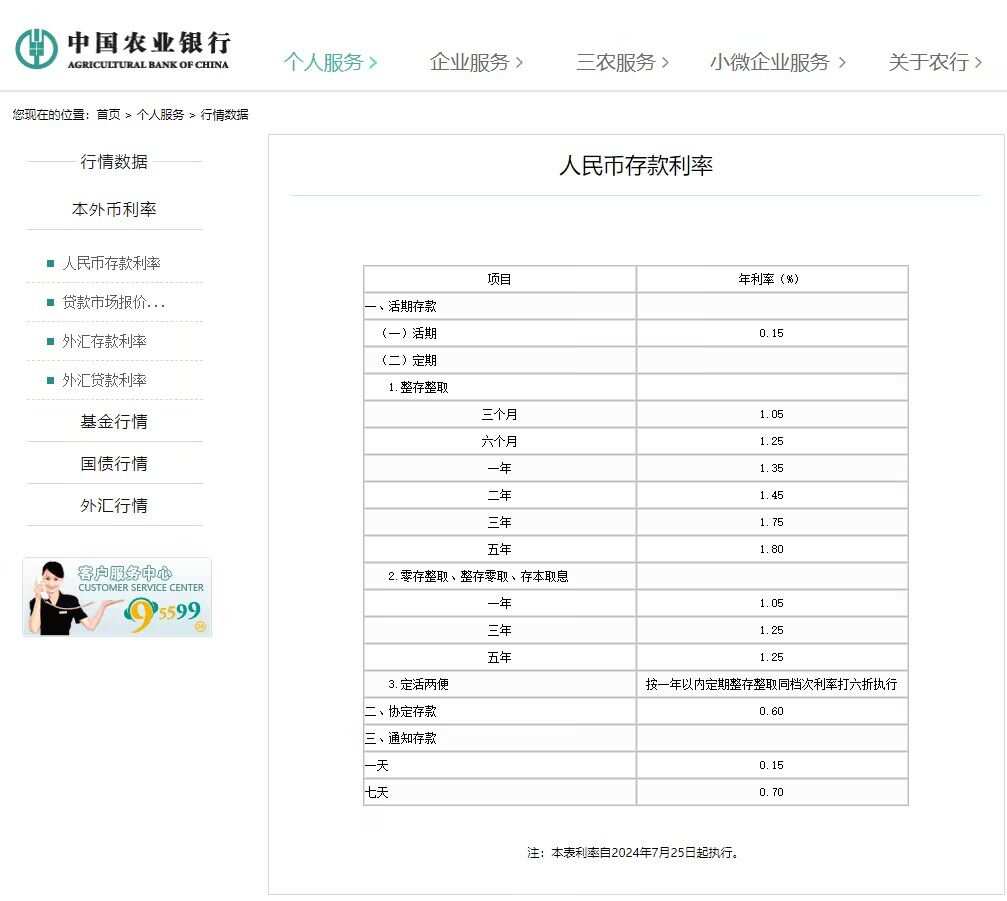
Among them, ICBC lowered the one-year, two-year, three-year and five-year renminbi time deposit rates to 1.35%, 1.45%, 1.75%, and 1.8%, respectively, down from the previous rates of 1.45%, 1.65%, 1.95%, and 2.00%. This is equivalent to a 10 basis point reduction for one-year time deposits, and a 20 basis point reduction for two-year, three-year, and five-year periods.
On Wednesday, July 24th Beijing time, according to the Economic Daily News, a major bank will lower deposit lending rates on July 25th, "with a 5 basis point reduction for current accounts, a 10 basis point reduction for terms of one year or less, and a 20 basis point reduction for terms of two years or more."
The report also said, "the bank website shows that its most recent lending rate adjustment was on December 22nd, 2023, with rates of 0.2% for current accounts, 1.15% for three-month terms, 1.35% for six-month terms, 1.45% for one-year terms, 1.65% for two-year terms, 1.95% for three-year terms, and 2.0% for five-year terms." It seems that all signs are consistent with ICBC's actions early in the morning.
After ICBC, another large state-owned bank, the Agricultural Bank of China, also announced a reduction in deposit lending rates, with one-year, two-year, three-year and five-year renminbi time deposit rates dropping to 1.35%, 1.45%, 1.75%, and 1.8%, respectively, down from the previous rates of 1.45%, 1.65%, 1.95%, and 2.00%. This is equivalent to a 10 basis point reduction for one-year time deposits, and a 20 basis point reduction for two-year, three-year, and five-year periods, which is the same as ICBC's action.
On Monday, July 22nd, the market welcomed the second interest rate cut of the year. The National Interbank Funding Center authorized by the central bank announced that as of that day, the one-year and five-year LPRs were both down by 10 basis points.
On Wednesday, the Beijing Business Daily reported that Bank of Communications has lowered its three-year fixed deposit rate from 2.6% to 2.5%, while other state-owned banks such as China CITIC Bank, Agricultural Bank of China, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, China Construction Bank, and Postal Savings Bank of China have not made any adjustments. "The execution rate is the final deposit rate that the bank has adjusted and is different from the lending rate."
However, it was later discovered by the media that Bank of Communications took the lead in lowering three-year deposit rates in Beijing, Shanghai, and other places after the "interest rate cut combination" this week. Although it fired the first shot of the large state-owned banks, it does not mean that a new round of deposit rate cuts has officially begun, but rather a regional adjustment of deposit rates, with different rhythms and magnitudes of adjustment.
After the recent official announcement of ICBC and Agricultural Bank of China's comprehensive reduction in deposit lending rates, the trend of state-owned banks leading the way in a "collective reduction of deposit lending rates" seems to have been fully formed, which is in line with analyst expectations.
For example, Dai Zhifeng, chief analyst of the banking sector at Zhongtai Securities, pointed out that from the recent adjustments of LPR and deposit rates, "every time the central bank lowers LPR twice, the major banks will lower lending rates twice," on the one hand, adjusting the liability side to match the asset side, while also opening up space for further downward adjustments of the asset side. Since 2024, the central bank has lowered LPR twice, but the major banks' lending rates have not been lowered since 2024. From the above rule, it can be expected that the deposit lending rates will be lowered in the near future.
Public data shows that since the establishment of the deposit rate market-oriented adjustment mechanism in 2022, commercial banks' deposit lending rates have collectively lowered four times. Although there is some time lag between small and medium-sized banks and large state-owned banks in terms of the rhythm, the overall trend remains unchanged:
To sum up, the concentration of state-owned banks in adjusting deposit lending rates is often seen as the starting point for a new round of deposit rate cuts. The last round of collective reductions in deposit rates occurred on December 22nd last year, when large state-owned banks such as ICBC, China Construction Bank, China CITIC Bank, Agricultural Bank of China, and Postal Savings Bank of China adjusted deposit lending rates, driving many national joint-stock banks and small banks to follow suit in a collective adjustment.
According to the China Fund News, small and medium-sized banks in Yunnan and Guangxi have begun to supplement their deposit rates. The types of products being adjusted not only include medium- and long-term deposits such as three-year and five-year periods, but also various short-term deposits. The rate reduction ranges from 5 to 40 basis points. However, this is not the starting point of a new round of deposit rate cuts, but rather a continuation of and supplement to the previous round of interest rate cuts for small and medium-sized banks.
At present, the market's consensus expectation is that there is still room for deposit rate cuts by banks:
Overall, although the deposit rates of commercial banks in China have been cut many times in recent years, based on the fact that the banking industry as a whole still faces pressure on net interest margins, market participants believe that there is still room for deposit rate cuts in the future.
For example, Zhou Maohua, a researcher with the macro group of the Financial Markets Department of China Everbright Bank, pointed out that in recent years, macroeconomic fluctuations, persistent bank concessions to the real economy, and fluctuations in financial asset prices have all contributed to the continued narrowing of net interest margins for banks, with some banks under greater pressure. At the same time, there is a structural imbalance in the domestic deposit market.
Some banks are making full use of the marketization mechanism of deposit interest rate to reprice deposits reasonably. On the one hand, this can alleviate the pressure of net interest margin and enhance the stability of bank operation. On the other hand, it can further reduce the financing cost of the real economy for banks.
The new round of 'deposit rate reduction' will still be led by large banks and followed by small and medium-sized banks, so as to ensure the stable and orderly development of the deposit market. However, the magnitude of the deposit rate cut is expected to remain relatively moderate.
Wang Yifeng, the chief analyst of the financial industry of Everbright Securities, believes that after this round of LPR rate cut, a new cycle of deposit rate reduction may be opened subsequently, which will drive the overall decline of the broad spectrum interest rate of deposits and loans. Lu Zhengwei, chief economist of Industrial Bank, also said that considering the stability of net interest margin, it is still necessary to further reduce the deposit interest rate while optimizing the LPR quote. Wang Qing, chief macro analyst of Dongfang Jincheng, said that the LPR quote in July was lowered, and according to the mechanism of market-oriented adjustment of deposit interest rate, the deposit interest rate of banks should be linked with the 1-year LPR quote and the 10-year national bond yield. This means that the deposit interest rate of banks will start a new round of comprehensive reduction, which will help stabilize the net interest margin of banks.
According to Brokerage China, on Tuesday morning, large-cap weighted stocks such as Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, Bank of China, China Yangtze Power, etc. set a new historical high, among which Industrial and Commercial Bank of China rose nearly 20% last year and the increase this year is also close to 35%, while Bank of China has risen three years in a row. Analysts interpreted the surge of bank stocks as the rumors of a deposit rate cut and the market's expectation of stable bank interest rate spread:
"Analysts believe that the sharp drop in bank stocks on Monday was due to the interest rate cut by the central bank, which was expected to narrow the bank's interest rate spread. However, after the market closed on Monday, the news that the deposit rate would be cut again was heard, and the market's expectations changed accordingly. The bank's interest rate spread may remain stable, which led to the rise of bank stocks on Tuesday."
On July 23, the bank sector rose against the trend, with a rise of 0.68%. Qilu Bank led the rise in bank stocks, with an increase of 4.02%. Industrial and Commercial Bank of China followed closely with a rise of 2.91%. Bank of China, Agricultural Bank of China, Chongqing Rural Commercial Bank, and China Construction Bank all rose by more than 2%. Among them, the stock prices of many banks such as Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, Agricultural Bank of China, and Bank of China reached a new high again.
