Shenwan stated that after resolving interest rate spread risks, Japanese life insurance companies still made a continuous positive contribution in the low interest rate era. In comparison, reducing debt costs is the main means for China to resolve interest rate spread risks; among them, reducing the reserved interest rate is the core method for reducing the new debt costs.
In the era of low interest rates, the operation of life insurance companies is facing challenges, and "risk transformation" is the core issue of the insurance industry, and the risk of interest spread loss is the top priority of "risk transformation".
In its report on August 16th, Shenwan Hongyuan Securities analyzed the solution to the risk of interest spread loss in Japan and compared the difference between the situation faced by insurance companies in China and Japan for reference.
 The Shenwan report pointed out that the main means for Japanese companies to resolve the risk of interest spread loss include: 1) lowering the predetermined interest rate (core); 2) optimizing product structure (core); 3) improving overseas asset allocation (core); 4) lengthening the duration of government bonds; 5) reducing operational costs; 6) lowering stock allocation.
The Shenwan report pointed out that the main means for Japanese companies to resolve the risk of interest spread loss include: 1) lowering the predetermined interest rate (core); 2) optimizing product structure (core); 3) improving overseas asset allocation (core); 4) lengthening the duration of government bonds; 5) reducing operational costs; 6) lowering stock allocation.
It is worth mentioning that after resolving the risk of interest spread loss, Japanese life insurance companies still achieved a sustained positive contribution to the triple difference in the era of low interest rates. In this process, insurance companies combined changes in customer needs under the trend of aging to promote the tilt of product structure towards guarantee types, further consolidating the positive contribution of death fee difference to profits.
What challenges have Japanese life insurance companies experienced?
In the early 1990s, the Japanese economic bubble burst, the GDP growth rate significantly declined, Japan entered a period of low interest rates, and insurance companies faced pressure on the asset side, liability side, and corporate operations.
Shenwan pointed out:
On the asset side:
1) Investment pressure: steeply declining long-term interest rates, sharp declines in stocks, rapid depreciation of US dollar assets, and a significant decline in yield centralization;
2) Exposure of stock assets: increase in non-performing loan ratio, significant decline in real estate prices, further dragging down investment performance.
On the liability side,
1) The growth rate of premiums weakened, and the number of policies, payment amount, and insurance amount per household continued to decline;
2) The quality of insurance policies has significantly declined;
3) With the increase of hedging sentiment and changes in customer demand,
On the corporate operation side,
1) Exposure to interest spread loss risk, significant decline in profits;
2) Eight life insurance companies in Japan have gone bankrupt, and mergers and acquisitions have become the main theme of the life insurance industry.
How does Japan resolve the risk of interest spread loss?
The main means for Japan to resolve the risk of interest spread loss include: 1) lowering the predetermined interest rate (core); 2) optimizing product structure (core); 3) improving overseas asset allocation (core); 4) lengthening the duration of government bonds; 5) reducing operational costs; 6) lowering stock allocation.
Shenwan Securities pointed out,
Japanese life insurance companies have significantly adjusted their asset allocation structure, and overseas securities have significantly increased their proportion. The Japanese life insurance industry has increased the proportion of overseas investment and relied on overseas high-yield assets to make up for the scarcity of high-yield assets in their home country. In 1990, overseas securities accounted for 13.07% of total Japanese life insurance investments and rose to 26.57% in 2021. It is expected to temporarily decline to 23.8% by 2022.
Overseas securities have continuously contributed excess profits to the investment portfolio of Japanese life insurance companies. From 2009 to 2022, the average investment yield of the general account of Japanese life insurance was 2.12%, while the average investment yield of overseas securities was 3.33%, which is 1.21 percentage points higher than that of the general account. In only two years, 2017 and 2019, the investment yield of overseas securities was lower than that of the general account by 0.40% and 0.26%, respectively, while in other years, significantly higher excess profits were contributed.
The core focus of the liability side is to lower the predetermined interest rate and optimize the product structure.
Continuously optimize the product structure to increase the proportion of protection-type and interest-sensitive products. With the trend of population aging, the demand for death insurance is decreasing, while the demand for medical security is continuously increasing. Japanese health insurance products have driven premium growth, and business proportion has increased from 8% in 1985 to 34% in 2015.
Under the influence of changes in product structure, the death loss partially offsets the interest margin loss. From 1990 to the early 2000s, the proportion of death loss income of the total three losses in the Japanese life insurance industry increased by 17 percentage points (life insurance companies adopted more conservative mortality tables when designing products, resulting in higher death losses, with a value rate of 2-3 times that of death insurance).
Additionally, Japan
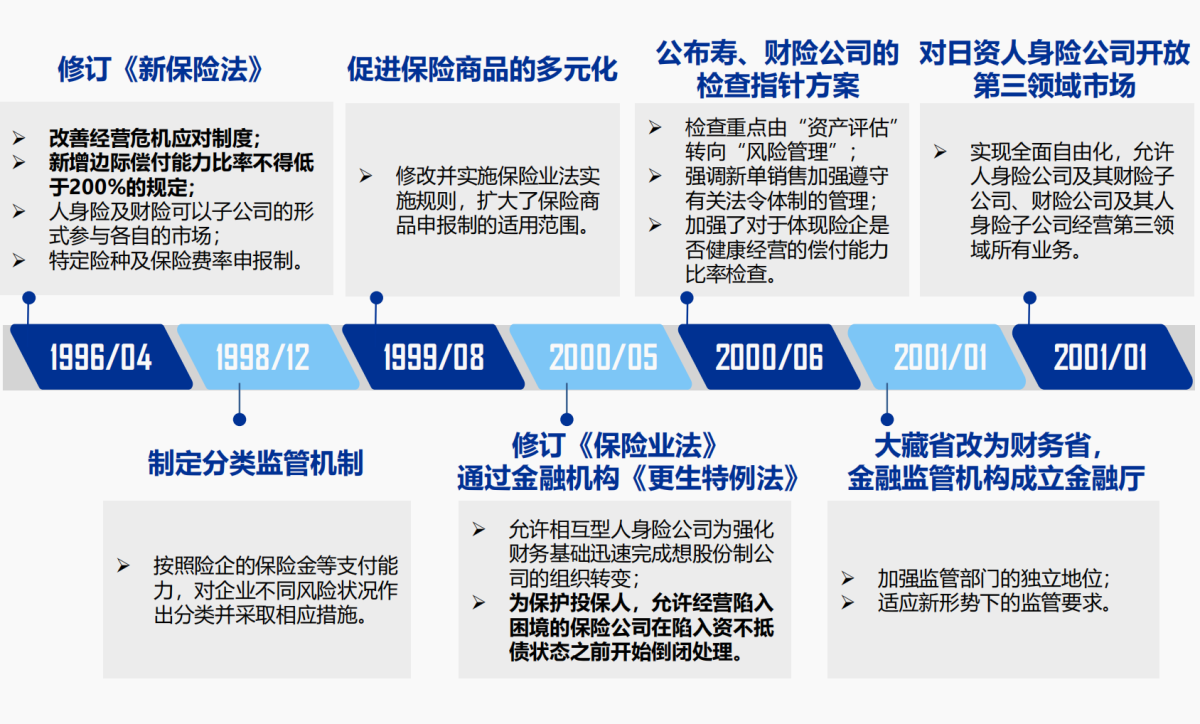
It is worth mentioning that,
After overcoming the interest margin loss crisis, Japanese life insurance companies continue to make positive contributions to their total three losses in a low-interest-rate environment. Japanese life insurance companies regard death loss and fee loss as the main source of profit, optimize the profit structure by increasing the proportion of protection-type products, improve the financial stability and profitability of the entire industry, and achieve long-term stable profitability level under a low-interest-rate environment.
Under the influence of changing customer demands and the optimization of profit structure by insurance companies, the company is developing a product structure that mainly focuses on protection-type products.

 申万报告指出,日本化解利差损风险的主要手段包括
申万报告指出,日本化解利差损风险的主要手段包括