We Think Anhui Expressway (HKG:995) Can Stay On Top Of Its Debt
We Think Anhui Expressway (HKG:995) Can Stay On Top Of Its Debt
Warren Buffett famously said, 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. As with many other companies Anhui Expressway Company Limited (HKG:995) makes use of debt. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
禾倫·巴菲特曾 famously 說過:'波動性與風險並不完全相同。' 在考察一家公司有多大的風險時,考慮其資產負債表是很自然的,因爲債務通常涉及到業務的崩潰。與許多其他公司一樣,皖通高速公司(HKG:995)也使用債務。但這種債務是否令股東感到擔憂?
When Is Debt A Problem?
什麼時候負債才是一個問題?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. Part and parcel of capitalism is the process of 'creative destruction' where failed businesses are mercilessly liquidated by their bankers. However, a more common (but still painful) scenario is that it has to raise new equity capital at a low price, thus permanently diluting shareholders. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
一般來說,只有當一家公司無法輕鬆償還債務時,債務才會真正成爲問題,要麼通過籌集資本,要麼通過自身現金流。資本主義的必然過程之一是「創造性摧毀」,失敗的企業會被它們的銀行家無情地清算。然而,一種更常見(但仍然痛苦)的情況是,公司不得不以低價籌集新的股本,從而永久性地稀釋股東的持股。當然,債務的好處在於,它通常代表着廉價資本,特別是當它代替公司中能夠以高回報率再投資的股份時。考慮一家企業使用了多少債務時,首先要看其現金和債務情況。
What Is Anhui Expressway's Net Debt?
皖通高速的淨債務是多少?
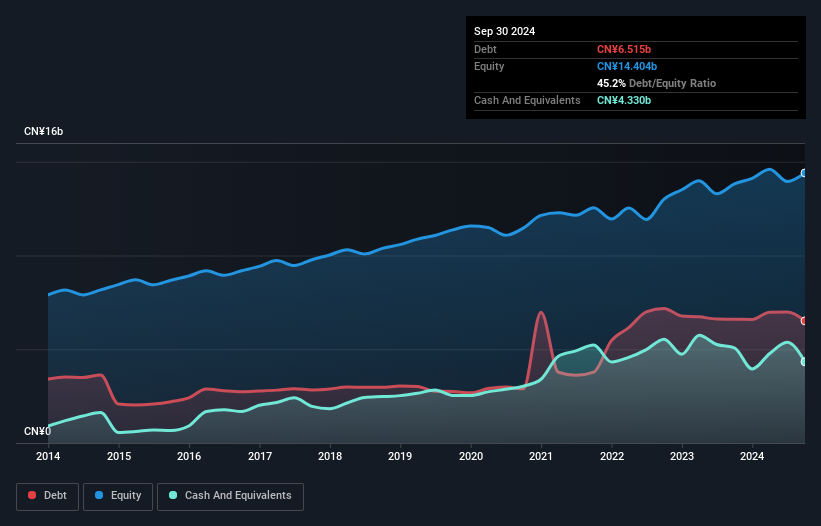
As you can see below, Anhui Expressway had CN¥6.52b of debt, at September 2024, which is about the same as the year before. You can click the chart for greater detail. On the flip side, it has CN¥4.33b in cash leading to net debt of about CN¥2.19b.
如你所見,截至2024年9月,皖通高速的債務爲65.2億港元,與前一年大致相同。你可以點擊圖表獲得更詳細的信息。另一方面,它擁有43.3億港元的現金,因此淨債務約爲21.9億港元。
How Strong Is Anhui Expressway's Balance Sheet?
皖通高速的資產負債表有多強?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Anhui Expressway had liabilities of CN¥2.35b due within 12 months, and liabilities of CN¥6.06b due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of CN¥4.33b as well as receivables valued at CN¥126.7m due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by CN¥3.95b.
根據最近報告的資產負債表,皖通高速在12個月內的負債爲23.5億人民幣,12個月後的負債爲60.6億人民幣。抵消這些義務的是其現金43.3億人民幣以及12個月內到期的應收款1270萬人民幣。因此,其負債超過現金和(短期)應收款總和39.5億人民幣。
Given Anhui Expressway has a market capitalization of CN¥20.7b, it's hard to believe these liabilities pose much threat. Having said that, it's clear that we should continue to monitor its balance sheet, lest it change for the worse.
考慮到皖通高速的市值爲207億人民幣,很難相信這些負債會構成很大威脅。不過,顯然我們應該繼續監控其資產負債表,以免情況變得更糟。
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
我們使用兩個主要的比率來告訴我們相對於收益的債務水平。第一個是淨債務除以利息、稅、折舊和攤銷前利潤(EBITDA),而第二個是其利潤前利息和稅(EBIT)覆蓋其利息費用的次數(或其利息覆蓋率,簡稱)。因此,我們考慮與折舊和攤銷費用相關的盈利以及沒有相關費用的盈利相對於債務水平。
Anhui Expressway has a low net debt to EBITDA ratio of only 0.71. And its EBIT easily covers its interest expense, being 71.7 times the size. So you could argue it is no more threatened by its debt than an elephant is by a mouse. On the other hand, Anhui Expressway saw its EBIT drop by 5.8% in the last twelve months. That sort of decline, if sustained, will obviously make debt harder to handle. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Anhui Expressway can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
皖通高速的淨債務與EBITDA比率僅爲0.71,屬較低水平。其EBIT輕鬆覆蓋利息支出,達到利息的71.7倍。因此你可以說,皖通高速所面臨的債務威脅並不比大象害怕老鼠更嚴重。另一方面,皖通高速在過去12個月中,其EBIT下降了5.8%。如果這種降幅持續下去,顯然將使債務變得更難處理。在分析債務時,資產負債表顯然是關注的重點。但是,最終業務的未來盈利能力將決定皖通高速能否隨着時間的推移加強其資產負債表。因此,如果您關注未來,可以查看這份免費的報告,了解分析師的盈利預測。
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. Looking at the most recent three years, Anhui Expressway recorded free cash flow of 44% of its EBIT, which is weaker than we'd expect. That's not great, when it comes to paying down debt.
但我們最後的考量也很重要,因爲公司不能用紙面利潤來償還債務;它需要冷硬的現金。因此我們總是檢查多少EBIT轉換爲自由現金流。從最近三年來看,皖通高速記錄的自由現金流佔其EBIT的44%,這比我們預期的要弱。這在償還債務時並不理想。
Our View
我們的觀點
The good news is that Anhui Expressway's demonstrated ability to cover its interest expense with its EBIT delights us like a fluffy puppy does a toddler. But truth be told we feel its EBIT growth rate does undermine this impression a bit. It's also worth noting that Anhui Expressway is in the Infrastructure industry, which is often considered to be quite defensive. All these things considered, it appears that Anhui Expressway can comfortably handle its current debt levels. On the plus side, this leverage can boost shareholder returns, but the potential downside is more risk of loss, so it's worth monitoring the balance sheet. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. For example, we've discovered 1 warning sign for Anhui Expressway that you should be aware of before investing here.
好消息是,皖通高速展示了其用EBIT覆蓋利息支出的能力,這讓我們像小狗對小孩的吸引力一樣感到高興。但說實話,我們認爲其EBIT增長率在一定程度上削弱了這一印象。值得注意的是,皖通高速處於製造行業,這通常被認爲相當防禦性。考慮到所有這些因素,皖通高速似乎能夠輕鬆處理其當前的債務水平。積極的一面是,這種槓桿可以提升股東回報,但潛在的缺點是風險更高,因此值得關注資產負債表。毫無疑問,我們從資產負債表中學到了大部分關於債務的知識。但最終,每個公司都可能存在資產負債表外的風險。例如,我們發現了皖通高速的一個警告信號,你在投資之前應該注意。
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
當然,如果您是那種喜歡購買沒有債務負擔的股票的投資者,那麼不要猶豫,立即發現我們獨家的淨現金增長股票列表。
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
對這篇文章有反饋嗎?對內容感到擔憂嗎?請直接與我們聯繫。或者,發送電子郵件至editorial-team @ simplywallst.com。
Simply Wall St的這篇文章是一般性質的。我們僅基於歷史數據和分析師預測提供評論,使用公正的方法,我們的文章並非意在提供財務建議。這並不構成買入或賣出任何股票的建議,並且不考慮您的目標或財務狀況。我們旨在爲您帶來基於基礎數據驅動的長期聚焦分析。請注意,我們的分析可能未考慮最新的價格敏感公司公告或定性材料。Simply Wall St對提及的任何股票都沒有持倉。

 According to the last reported balance sheet, Anhui Expressway had liabilities of CN¥2.35b due within 12 months, and liabilities of CN¥6.06b due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of CN¥4.33b as well as receivables valued at CN¥126.7m due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by CN¥3.95b.
According to the last reported balance sheet, Anhui Expressway had liabilities of CN¥2.35b due within 12 months, and liabilities of CN¥6.06b due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of CN¥4.33b as well as receivables valued at CN¥126.7m due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by CN¥3.95b.