大摩認爲,特朗普的移民和關稅政策,將導致美國經濟在明年面臨增長放緩和通脹頑固的雙重挑戰:GDP增速放緩至1.9%,核心PCE通脹保持在2.5%的高位。聯儲局對利率路徑保持謹慎,預計在明年二季度開始暫停減息。
特朗普的一系列政策主張,給美國經濟蒙上一層厚厚的迷霧。摩根士丹利認爲,明年全球市場可能會迎來一個經濟增長放緩而通脹更加頑固的美國。
摩根士丹利經濟學家Seth B Carpenter團隊在最近公佈的前瞻報告中警告,若特朗普兌現收緊移民政策、加徵關稅的承諾,美國勞動力市場和貿易都將受到衝擊,未來兩年美國GDP增長承壓,通脹下行之路更加坎坷。
 考慮到初步的通脹壓力和特朗普政策的不確定性,大摩預計,聯儲局對未來的利率路徑保持謹慎,並在明年二季度開始暫停減息。而隨着經濟放緩增長,2026年下半年就業增長几乎停滯,屆時聯儲局預計將重啓減息。
考慮到初步的通脹壓力和特朗普政策的不確定性,大摩預計,聯儲局對未來的利率路徑保持謹慎,並在明年二季度開始暫停減息。而隨着經濟放緩增長,2026年下半年就業增長几乎停滯,屆時聯儲局預計將重啓減息。
經濟壓力山大
鑑於更嚴格的移民政策和高關稅對經濟造成了巨大壓力,摩根士丹利預計,2025年美國GDP增長將從2024年的2.4%放緩至1.9%,2026年進一步降至1.3%。
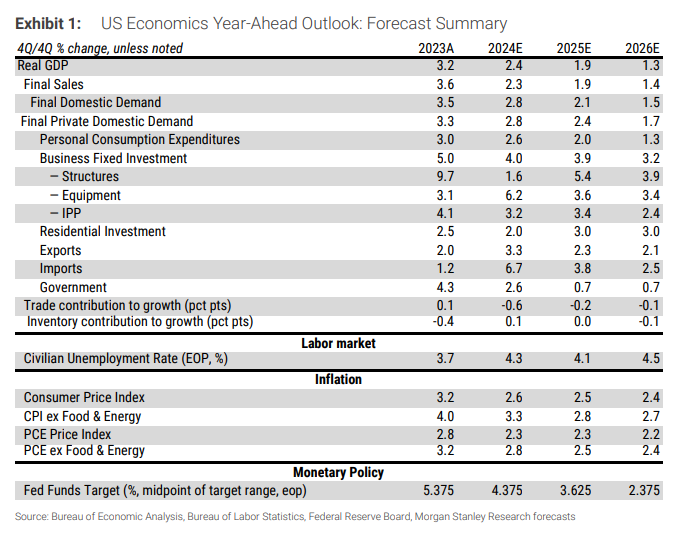
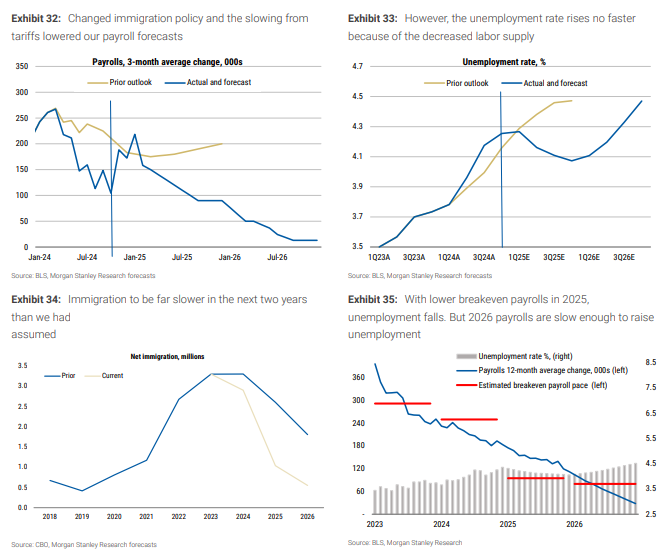
大摩認爲,新政府對非法移民的驅逐和排斥,將導致淨移民人數從2023年的330萬下降至2026年的50萬。移民的減少預計將使勞動市場在2025年保持緊張狀態,但隨着經濟增長低於潛在水平,失業率在2026年將上升。
根據大摩估計,到2024年年末失業率爲4.3%,2025年爲4.1%,2026年爲4.5%。移民減少意味着2025年和2026年的就業人數顯著下降。
儘管消費者基礎依然穩固,但由於勞動力市場降溫、關稅上升和移民減少等因素,消費增長預計將在2025年和2026年顯著放緩。
大摩預計,2024年實際消費增長爲2.6%,2025年下降至2.0%,2026年爲1.3%。與服務消費相比,商品消費的下降幅度較小,因爲較低的利率支持耐用品消費。
在財政政策方面,摩根士丹利認爲,2025年的財政支出的勢頭將有所減弱,新政府雖然會通過稅收立法,但主要是維持現有的減稅政策,而非刺激經濟增長。
商業投資明年保持穩定增長,AI投資對GDP或有更大貢獻
過去幾年,商業投資僅限於特定行業,比如2023年的製造業投資熱、2024年的AI投資潮。
特別是,AI相關的投資在過去一年中顯著加速,大摩預計這一趨勢將在2025年和2026年持續。AI投資的增長預計將對數據中心、電力結構和相關技術設備的投資產生積極影響,直接貢獻於GDP的增長。
大摩預計,實際商業固定投資將在2024年增長4.0%,2025年增長3.9%,2026年增長3.2%;結構投資在今明兩年的增速分別爲1.6%和5.4%(其中一半由AI貢獻)。
AI已經開始推動數據倉庫和與電力相關的結構投資。摩根士丹利預計,數據倉庫和電力相關的投資將進一步加速。
我們預計AI的強勁表現將貢獻2025年結構投資增長的大約一半。 對於2026年,我們預計增長將放緩至4%。
與2025年相比,AI相關的結構支出在2026年的貢獻大致相同(3.5個百分點)。然而,與關稅相關的不利因素使增長減少了四分之三個百分點。
大摩預計,AI投資將在2024年將美國GDP提高0.1個百分點。
報告指出,2023年初,數據中心結構的投資出現上升趨勢,電力建設和計算機投資在2023年中也有所增長。這三類商業投資可能表明投資加速的效果。對電力相關結構和數據中心的額外投資直接推動了GDP增長。然而,AI相關設備的投資主要依賴於進口,國內計算機支出的75%用於進口,額外的電池存儲幾乎完全依賴進口,因此目前AI設備支出對GDP的正面影響在很大程度上被進口抵消。
預計到2025年,AI投資將對經濟增長產生更大的推動,預計增加0.25個百分點。數據倉庫(Data Warehouse)和電力結構的支出將爲結構投資貢獻3.5個百分點,並對GDP貢獻十分之一。儘管進口增長較快,但在計算機及相關設備上的支出也將做出類似貢獻。
而到了2026年,由於數據中心建設增長放緩,AI投資對GDP增長的貢獻可能降至0.15個百分點。
高進口關稅下,貿易承壓
未來兩年,特朗普的高進口關稅政策預計將對進口構成壓力,而墨西哥增長放緩和美元走強的前景預計將導致出口放緩。
大摩預計,貿易將在2025年對GDP增長產生輕微拖累(-0.2個百分點),但在2026年影響將減少(-0.1個百分點),因爲進口增長放緩。
儘管關稅對進口構成壓力,但AI投資的持續增長預計將支持進口,特別是在2025年和2026年。大摩稱,美國公司將繼續尋找用於AI研究、開發和基礎設施的專用硬件、先進電子設備和其他技術組件。

更頑固的通脹
摩根士丹利預計,通脹在2025年第一季度之前繼續減速,但之後變得更加頑固。
具體來看,美國核心PCE通脹率將在2024年降至2.8%,但由於勞動市場緊張和高關稅政策,該數字將在2025年和2026年保持在2.5%和2.4%的較高水平,仍高於聯儲局的目標水平。
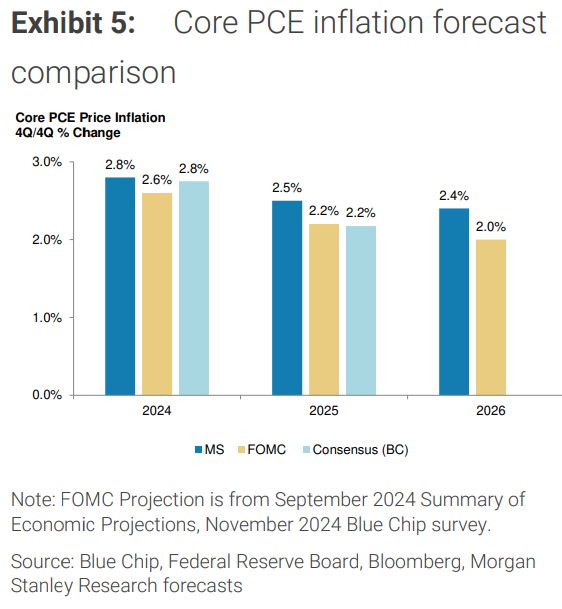
大摩認爲,加徵關稅預計將在2025年晚些時候對通脹產生更明顯的影響,而勞動力市場的緊張則可能在2025年推動工資增長,從而對服務業通脹造成壓力。
更謹慎的減息路徑
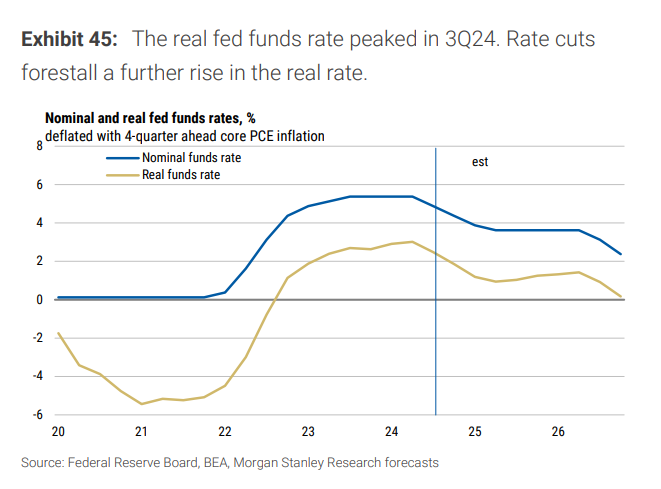
熱愛貨幣寬鬆的特朗普上臺,一不小心就可能點燃通脹,聯儲局必須對未來的利率路徑慎之又慎。
摩根士丹利預計,聯儲局將在2025年上半年繼續減息,每次減息25個點子,直至聯邦基金利率降至3.625%。然而,隨着勞動力市場的緊張和服務業通脹的壓力,以及殘餘季節性因素的影響,聯儲局可能會在2025年5月後暫停減息。同時,聯儲局將在明年一季度結束量化緊縮(QT)。
只有在通脹穩定並開始下降,經濟增長因關稅而顯著放緩後,聯儲局才可能在2026年下半年恢復減息。大摩預計,到2026年底,聯邦基金利率將降至2.375%。
摩根士丹利對於2025年美國利率前景進行了假設:
情景1:美國硬着陸 – 中性利率低於預期,聯儲局過度緊縮。貨幣政策滯後,在2025年一季度才開始影響經濟,導致經濟急劇放緩,通脹低於目標,形成硬着陸。
這種情況下,大摩預計,聯儲局在2025年上半年迅速將利率降至1%,並保持至2026年下半年。預測2025年GDP增長爲-0.3%(按季度同比),2026年爲1.8%。
情景2:美國再加速 – 經濟在2025年因減息而反彈。中性利率高於預期,聯儲局減息過多,經濟重新加速,通脹因此上升。
在這一情景中,生產率增長更強,中性利率持續較高。大摩預計,在政策利率降至3.625%後,聯儲局將在2025年四季度再次加息,在2025年末將利率提高至3.875%,並在2026年末將利率進一步提高至4.875%。預測2025年GDP增長爲2.8%(按季度同比),2026年爲2.3%。

 考虑到初步的通胀压力和特朗普政策的不确定性,大摩预计,
考虑到初步的通胀压力和特朗普政策的不确定性,大摩预计,