① In the investors of Tianyu Semiconductors, Hubble, BYD, and Chenda Capital have all appeared. ② In terms of gross margin, the 6-inch epitaxial wafer gross margin of Tianyu Semiconductors has declined, standing at 23.3%, 23.7%, 20%, and 5.7% respectively. ③ Recently, the listing process for semiconductor companies such as Tianyu Semiconductors, Yingrun Technology, Jingcun Technology, Herun Electronics, Zhuohai Technology, InnoSense, and Qiangyi Semiconductors has entered a new stage.
According to the Star Daily on December 24 (Reporter Chen Mei), after InnoSense, another semiconductor company has made a move toward the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. Recently, Guangdong Tianyu Semiconductor Co., Ltd. submitted a listing application to the Main Board of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange.
The prospectus shows that Tianyu Semiconductors is a Silicon Carbide epitaxial wafer company, positioned upstream in the Semiconductors Industry Chain. A semiconductor investor told the Star Daily reporter that the quality of Silicon Carbide epitaxy directly affects the performance of Silicon Carbide devices.
 Currently, the main suppliers of Silicon Carbide epitaxial wafers globally include international companies such as Japan's Rohm, Japan's Showa Denko, Swiss STMicroelectronics, and South Korea's SK Siltron, while domestically, there are China's Tianyu Semiconductors, Xiamen Hantian Technology Electronics, and China Electronics Technology Semiconductors.
Currently, the main suppliers of Silicon Carbide epitaxial wafers globally include international companies such as Japan's Rohm, Japan's Showa Denko, Swiss STMicroelectronics, and South Korea's SK Siltron, while domestically, there are China's Tianyu Semiconductors, Xiamen Hantian Technology Electronics, and China Electronics Technology Semiconductors.
With a valuation of 10 billion, a unicorn has emerged from Dongguan.
Rewinding back to more than a year ago, Tianyu Semiconductors secured approximately 1.2 billion yuan in financing, with investors including China Belgium Fund, Guangdong Yuke Investment, Nam Cheong Industrial Investment Group, Guangdong Jiayuan Technology, China Merchants Capital, and Qianchuang Capital.
Even earlier, in July 2021, Hubble Investment became the first investor to enter Tianyu Semiconductors. At that time, Hubble Investment contributed 70 million yuan to participate in the angel round of financing. Afterwards, BYD, Chenda Capital, Shangqi Capital, and a number of industrial capital participated in the A round financing of Tianyu Semiconductors.
The Star Daily reporter noted that in the A round of financing, three major investment institutions: BYD, Chenda Capital, and Shangqi Capital, are all related to the New Energy Vehicles Industry. Among them, the main investor of Chenda Capital is Contemporary Amperex Technology, which has primarily invested in Energy Electrical Utilities, advanced manufacturing, and automotive transportation fields in recent years.
The aforementioned semiconductor investment individuals told the Star Daily reporter that the raw material for silicon carbide (SiC) epitaxy, silicon carbide (SiC), is a third-generation semiconductor material primarily used in 5G, Internet of Things, and electric vehicle fields. The earliest to invest were Hubble Investment and CVC institutions from the New Energy Industry Chain, mostly attracted by the application of silicon carbide (SiC) in these fields.
In the prospectus, the Star Daily reporter noticed that Tianyu Semiconductor stated that benefiting from the development of downstream application markets such as xEV (electric vehicles) and Solar + ESS (Energy Storage Systems), has driven the silicon carbide power semiconductor device industry.
Tianyu Semiconductor claimed that the xEV industry has shown strong compound annual growth rates from 2019 to 2023, reaching 66.7%; and is expected to increase to 36.2% from 2023 to 2028.
Against this industry background, after raising 1.2 billion yuan in financing in 2023, Tianyu Semiconductor's valuation broke through 10 billion yuan at once, approaching 13 billion yuan, becoming a "super unicorn" in Dongguan, Guangdong.
Orders from South Korean clients have decreased, causing fluctuations in Tianyu Semiconductor's performance.
Benefiting from the growth of the aforementioned three major industries, Tianyu Semiconductor's revenue has also doubled from 2021 to the first six months of 2024. During the reporting period, the revenues were approximately 0.155 billion yuan, 0.437 billion yuan, 1.171 billion yuan, and 0.361 billion yuan; meanwhile, the company’s net income was -0.18 billion yuan, 2.814 million yuan, 95.882 million yuan, and -141 million yuan respectively.
The Star Daily reporter noted that in 2023, Tianyu Semiconductor's revenue and net income grew significantly, attributed to receiving large orders from South Korean clients that year. The prospectus showed that the order amount from this client in South Korea reached 0.491 billion yuan in 2023, accounting for 42% of total revenue, with the order demand being for 6-inch epitaxy.
However, in the first six months of 2024, the order amount from this client in South Korea decreased to 35.96 million yuan, with its share of total revenue also shrinking to 10%. It is worth mentioning that during the reporting period, most of Tianyu Semiconductor's large orders were for 6-inch epitaxy.
Regarding the revenue growth of 6-inch epitaxial wafers, Tianyu Semiconductors believes it is mainly due to relatively mature technology and better cost-effectiveness.
However, Tianyu Semiconductors experienced fluctuations in gross margin. During the reporting period, the gross margin for its 6-inch epitaxial wafers declined, with figures of 23.3%, 23.7%, 20%, and 5.7%; in contrast, the gross margin for 4-inch semiconductor epitaxial wafers showed an upward trend, with figures of 13.8%, 16.5%, 53.2%, and 30.4%. The overall gross margin during the reporting period were 15.7%, 20.0%, 18.5%, 19.4%, and 12.1%.
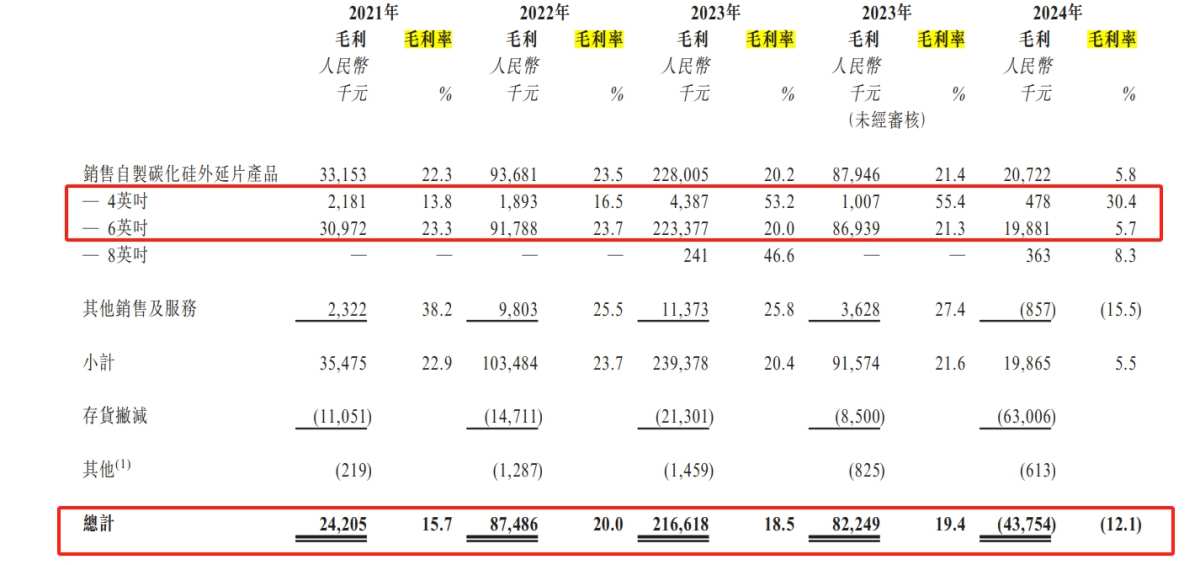
The decline in gross margin is related to market competition, weak demand, and falling raw material prices. Tianyu Semiconductors candidly stated in its prospectus that regarding the average selling price of epitaxial wafers, the company strategically lowered prices to increase market penetration, leading to a drop in the price of Silicon Carbide epitaxial wafers.
"Additionally, constrained by technological advances and efficiency advantages, the 4-inch epitaxial wafer market is expected to further shrink, decreasing from 54,000 pieces in 2023 to 20,000 pieces in 2028, with a compound annual growth rate of -17.8%. In the context of intensified competition, the average selling price of 6-inch Silicon Carbide epitaxial wafers is also expected to drop from 9,377 yuan per piece in 2021 to 6,560 yuan per piece in 2028," said Tianyu Semiconductors.
Domestic semiconductor companies are racing to go public.
In addition to Tianyu Semiconductors, reporters from the Science and Technology Innovation Board Daily noted that recently, domestic semiconductor companies are flocking to rush for IPOs, with the listing processes of companies like Yingrun Technology, Jingcun Technology, Herun Electronics, Zhuohai Technology, InnoSec, and Qiangyi Semiconductors entering a new phase.
Among them, Gallium Nitride power semiconductor company InnoSec has initiated its IPO, with STMicroelectronics, Jiangsu State-owned Enterprise Mixed Ownership Reform Fund, Dongfang Chuanglian, and Suzhou High-End Equipment as cornerstone investors, subscribing for 0.1 billion dollars of the offered shares.
Before the IPO, InnoSec attracted attention from a number of investment institutions including Dongfang State-owned Assets, Zhuhai High-tech Investment, Yida Capital, Haifu Industrial Fund, and China-Belgium Direct Private Equity Investment Fund.
In addition, companies like Yingrun Technology, Jingcun Technology, Herun Electronics, Zhuohai Technology, and Qiangyi Semiconductors have all started their IPO sprint, currently at stages such as listing guidance filing and IPO guidance acceptance.
Apart from the IPO sprint, semiconductor companies are also the hottest targets in the merger and acquisition field.
Why are domestic semiconductor companies all rushing for IPOs? In an interview with a reporter from the Star Daily, Zhi Peiyuan, vice chairman of the Investment Professional Committee of the China Investment Association, said that the frequent occurrences of IPO sprints in the semiconductor industry reflect the deep-seated capital needs of enterprises.
Through such financial operations, semiconductor companies aim to obtain sufficient funds to meet high-intensity R&D investments, capacity expansion, and technology iteration, thus consolidating their market position, according to Zhi Peiyuan.
Looking at Tianyu Semiconductors and Innovatech, which have already disclosed their prospectuses, the Star Daily reporter noticed that their operating cash flows were not very stable. Specifically, the net cash generated from operating activities for Tianyu Semiconductors dropped from 0.201 billion yuan in the first half of 2023 to 85.94 million yuan in the first half of 2024, while this figure was negative in 2021 and 2022.
Meanwhile, from 2021 to 2023, Innovatech's operating cash flows were -0.56 billion yuan, -0.936 billion yuan, and 5.93 million yuan, respectively.
From the perspective of long-term industry development, Zhi Peiyuan believes that capital operations like IPOs can not only alleviate immediate financial pressure but also represent a long-term development strategy choice.
Currently, China's semiconductor industry is in a period of rapid development. Although breakthroughs have been made at multiple levels, challenges still remain in key technologies such as chip design, advanced manufacturing equipment, and wide bandgap semiconductor materials like Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN). In particular, critical links such as EDA software, Lithography, and special chemicals urgently need independent research and innovation breakthroughs, and these areas also need more funding support.

 “目前,全球主要碳化硅外延片供应商,包括日本的罗姆ROHM、日本的昭和电工、瑞士的意法半导体集团、韩国的SK Siltron等国际企业,国内则有中国的天域半导体、厦门的瀚天天成电子和中电科半导体等。”
“目前,全球主要碳化硅外延片供应商,包括日本的罗姆ROHM、日本的昭和电工、瑞士的意法半导体集团、韩国的SK Siltron等国际企业,国内则有中国的天域半导体、厦门的瀚天天成电子和中电科半导体等。”