Since the beginning of this year, in the pharmaceuticals Sector, the Hong Kong stock market has demonstrated more cost-effective investment value compared to the A-shares.
Since the beginning of this year, in the pharmaceuticals Sector, the Hong Kong stock market has demonstrated more cost-effective investment value compared to the A-shares.
From the performance in the first half of 2024, influenced by multiple factors such as macroeconomic conditions, the high base from last year's sector, and the introduction of the USA Biodefense Act, the pharmaceutical sectors in both AH markets have experienced a pullback. However, due to differences in investor structure and liquidity between the two markets, the degree of pullback varies. As of June 30, 2024, the China Securities Pharmaceutical Index, Hang Seng Healthcare Index, and Hang Seng Hong Kong-Listed Biotech Index fell by 20.0%, 27.6%, and 27.8% respectively compared to the end of 2023.
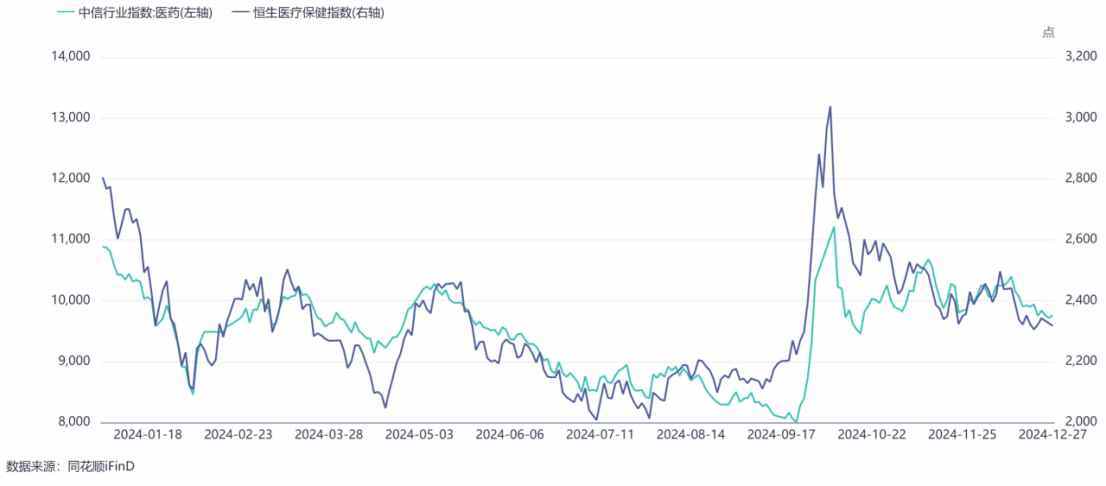
 In the second half of this year, the fluctuations in the pharmaceutical sectors of the AH markets have also been different. From the performance in Q3 this year, as of September 30, the China Securities Pharmaceutical Index and the Hang Seng Healthcare Index fell by 5.6% and 4.9% respectively. Over the three-month period, the decline in the Hong Kong stock pharmaceutical sector was significantly less than that in the A-share market, indicating that the Hong Kong stock market has emerged from the market bottom earlier than the A-share market; as of December 27, the declines of the China Securities Pharmaceutical Index and the Hang Seng Healthcare Index were 10.75% and 19.48% respectively. In terms of the extent of the drop, the Hong Kong stock pharmaceutical sector undoubtedly offers better cost-effectiveness.
In the second half of this year, the fluctuations in the pharmaceutical sectors of the AH markets have also been different. From the performance in Q3 this year, as of September 30, the China Securities Pharmaceutical Index and the Hang Seng Healthcare Index fell by 5.6% and 4.9% respectively. Over the three-month period, the decline in the Hong Kong stock pharmaceutical sector was significantly less than that in the A-share market, indicating that the Hong Kong stock market has emerged from the market bottom earlier than the A-share market; as of December 27, the declines of the China Securities Pharmaceutical Index and the Hang Seng Healthcare Index were 10.75% and 19.48% respectively. In terms of the extent of the drop, the Hong Kong stock pharmaceutical sector undoubtedly offers better cost-effectiveness.
The reason for this may be that in the Hong Kong stock pharmaceutical sector, the weight of 18A companies, which are more sensitive to policy and interest rate changes, is larger than that in the A-share market. Coupled with the more advantageous chip structure of the Hong Kong stock market, this ultimately gives the Hong Kong stock pharmaceutical sector a higher value proposition.
Behind the warming of Hong Kong stock pharmaceutical IPOs.
Recently, there have been significant signs of recovery in Hong Kong medical IPOs, in stark contrast to the first half of the year. In the first half of this year, only five medical companies successfully listed in Hong Kong, reflecting a low IPO approval environment, but this situation has changed significantly in the second half of the year.
According to Zhituo Finance APP observation, as of December 27, the total number of enterprises applying for IPO approval in the Hong Kong medical sector reached 51, a growth of over 30% compared to 39 last year, with the number of first-time applications remaining steady at 25, close to last year's 24.
Looking at the performance of each quarter this year, the number of Hong Kong medical companies applying for IPOs in the first three quarters of 2024 was basically the same as the same period last year. It was not until Q4 that, benefiting from the stimulating policies of the Chinese capital markets since September, the number of applying enterprises saw a significant increase. In November, nine medical and health companies submitted prospectuses, and in the first half of December, an additional five companies applied, setting a record for the year.
The apparent warming of Hong Kong medical IPOs may be related to the policy movements in both AH markets as well as the overall IPO issuance performance in Hong Kong.
On one hand, from the policy perspective, since the China Securities Regulatory Commission announced a phase of tightening the IPO rhythm in August 2023, the entry standards for IPOs have become increasingly strict, with significant slowdowns in the acceptance of IPO applications, reviews, and other processes. Previously, the A-share Star Board modified the listing approval standards for medical companies, changing the cumulative R&D investment amount in the last three years from "60 million yuan or above" to "80 million yuan or above"; the number of 'invention patents' from "over 5" to "over 7"; and the 'compound annual revenue growth rate in the last three years' from "20%" to "25%". Additionally, besides operation and financial performance, sales compliance and innovation attributes have also become key focuses in the Star Board's listing review.
Under this policy adjustment, some biomedical companies queuing for listing chose to voluntarily withdraw their applications. Data shows that, as of now, a total of 25 new stocks have listed in the A-shares, of which only two are from the medical sector, while over 50 medical enterprises from the three major exchanges have chosen to terminate their reviews. In light of the suddenly increasing IPO demand, Hong Kong undoubtedly becomes an important option to meet this demand.
As for Hong Kong, on April 19 this year, the China Securities Regulatory Commission released five measures for collaboration in the capital market with Hong Kong; on October 18, the Hong Kong Securities Regulatory Commission and the Hong Kong Stock Exchange jointly announced the optimization of the timeline for new listing application approval processes. These measures provided policy support and facilitation for mainland medical and health enterprises to list in Hong Kong, encouraging more medical care enterprises to choose Hong Kong stock as the IPO pathway.
On the other hand, since the second half of this year, as the performance of the Hong Kong market has improved, new IPOs have received more positive responses from the market. For medical enterprises, this emerging market trend will help alleviate the contradiction between the past high valuations in financing and the enthusiasm of market investors.
From the data, although based on the current IPO situation in Hong Kong, the estimated number of companies expected to list on the Main Board through IPOs in the entire 2024 fiscal year will be between 67 to 69, which is roughly the same as the 68 last year, the corresponding net fundraising amount has significantly increased. As of the third week of December, there are 62 new IPO companies listed on the Main Board of Hong Kong, corresponding to a net fundraising amount of 71.628 billion HKD, which is 89.95% higher than last year's 37.708 billion HKD. Additionally,
In the second half of this year, the average subscription multiple for international placements of Hong Kong stocks IPOs reached 4.19 times, up from 1.56 times in the first half of the year, clearly indicating that the market's activity level has significantly increased, making it an important reference factor for domestic pharmaceutical companies choosing the Hong Kong stock market.
The differentiation in 18A is quite pronounced, with funds focusing on leading value.
As mentioned earlier, the higher value proposition of Hong Kong pharmaceutical companies largely comes from the 18A sector, but entering 18A does not mean all is well; on the contrary, only by demonstrating leading value can funds show interest.
According to Zhichun Finance APP, currently, about 80% of the Hong Kong pharmaceutical sector consists of small-cap companies with a market cap of less than 1 billion HKD, with significant disparities in market capitalization within the sector. Under this dual factor, most individual stocks have extremely poor trading liquidity, a trend more pronounced in 18A companies.
Especially in the nearly three years after 2021, the average and median monthly transaction volumes of the Hong Kong pharmaceutical sector were 146.6 billion HKD and 128.1 billion HKD respectively, corresponding to an average daily transaction volume of only 6.6 billion HKD, which only increased to an average of 8.8 billion HKD in Q4 of this year. For 18A, this is a 'wolf is many and meat is few' issue, which also causes Hong Kong funds to place more importance on the leading value exhibited by enterprises, exacerbating the differentiation within 18A.
Statistical data shows that among the 66 listed Hong Kong stocks 18A companies, a total of 20 companies have a market cap of less than 1 billion HKD, accounting for 31%; 21 companies have a market cap of 1-3 billion HKD, accounting for 32%. It is worth noting that, apart from the leading 30% of companies, the remaining 70% of 18A companies have seen their valuations decline by over 50% from historical highs, with most companies having an average daily trading volume of less than 1 million HKD, and some even only a few tens of thousands of HKD.
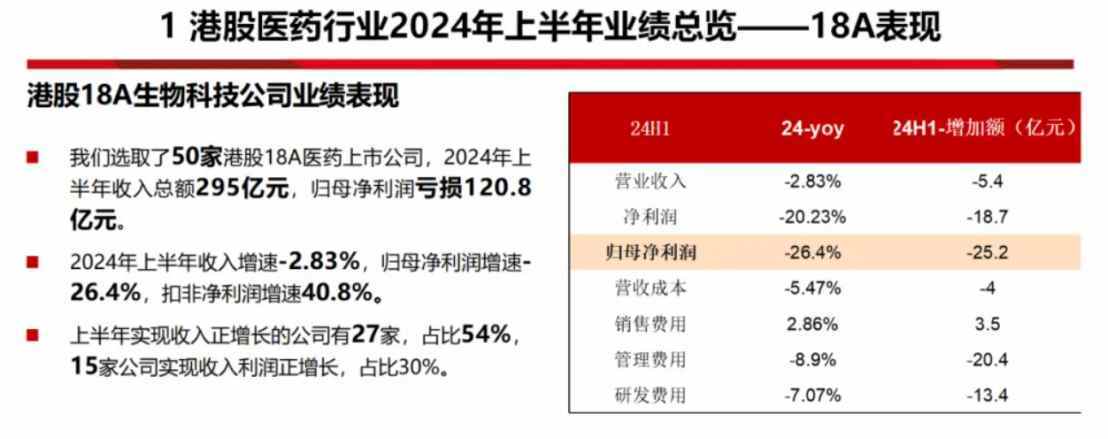
According to data from Southwest Securities, the total revenue of the 50 selected sample 18A companies for the first half of 2024 is 29.5 billion yuan, with a net loss of 12.08 billion yuan attributable to the parent company; the revenue growth rate for the first half of this year is -2.83%, and the net profit growth rate attributable to the parent company is 26.4%, while the net profit growth rate excluding non-recurring items is 40.8%. In the first half of this year, 27 companies achieved positive revenue growth, accounting for 54%; 15 companies achieved positive revenue and profit growth, accounting for 30%.
Although the performance of leading companies varies, most are in sectors characterized by innovation, scarcity, defensive attributes, and high dividends and payouts. For example, in the last two years in the Hong Kong stock market's 18A, BEIGENE (06160), as a relatively mature Biopharma company, has become the company with the highest Market Cap in the Hong Kong stock market's 18A. Additionally, leading innovative Pharmaceutical companies in the Hong Kong stock market's 18A, such as EVEREST MED-B (01952), HENLIUS (02696), ASCENTAGE-B (06855), and SKB BIO-B (06990), have seen remarkable stock price increases while continuously releasing their innovation value.

Guosen Securities Research indicates that from the supply side, the industry is undergoing a significant supply-side structural reform and is expected to enter a new growth cycle by 2025. The proportion of industry losses has been rising year by year since 2019, stabilizing at over 30% this year. The medical industry continues to be affected by external factors, such as macroeconomics, geopolitical dynamics, and healthcare cost control policies. Leading companies have demonstrated resilience during this industry clearing period, further increasing market share, and are expected to exhibit stronger competitiveness after the industry rebounds.

 而在今年下半年,AH两地医药板块的波动表现也并不相同。从今年Q3季度表现看,截至9月30日,中信医药指数和恒生医疗保健指数分别下跌5.6%和4.9%,在三个月的时间,港股医药跌幅缩窄幅度远大于A股跌幅,说明港股较A股更早走出市场底部;而截至12月27日,中信医药指数和恒生医疗保健指数跌幅分别为10.75%和19.48%。从下探幅度来说,目前港股医药无疑更具配置性价比。
而在今年下半年,AH两地医药板块的波动表现也并不相同。从今年Q3季度表现看,截至9月30日,中信医药指数和恒生医疗保健指数分别下跌5.6%和4.9%,在三个月的时间,港股医药跌幅缩窄幅度远大于A股跌幅,说明港股较A股更早走出市场底部;而截至12月27日,中信医药指数和恒生医疗保健指数跌幅分别为10.75%和19.48%。从下探幅度来说,目前港股医药无疑更具配置性价比。