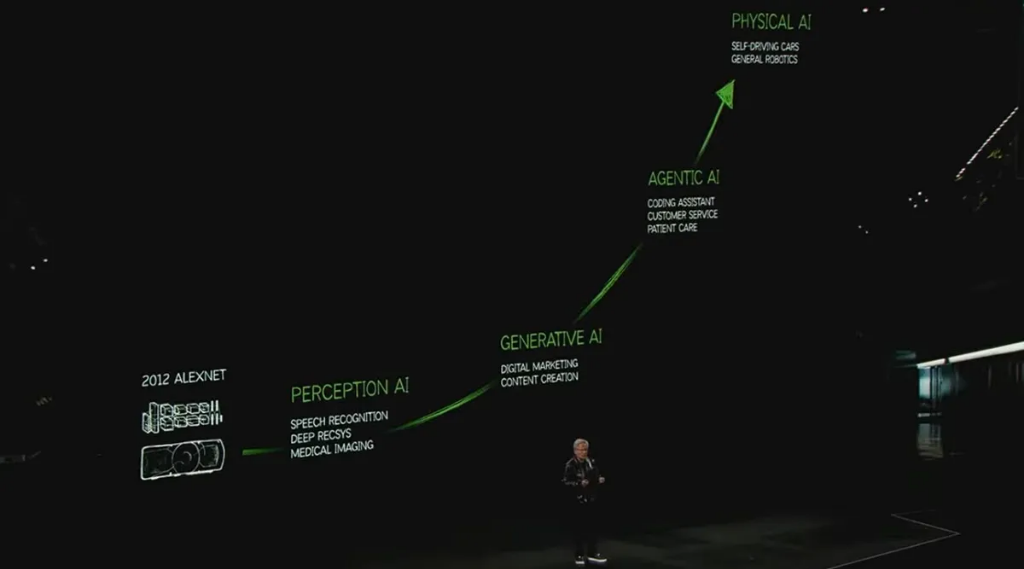
Physical AI grants robots stronger environmental perception, understanding, and interaction abilities. At the CES conference, Huang Renxun stated that physical AI will completely transform the $50 trillion manufacturing and Logistics sectors, "the 'ChatGPT moment' in the field of robots is approaching."
Author: Zhang Yaqi.
Source: Hard AI.
 Will robots soon have their "ChatGPT moment"? NVIDIA will heavily release the Cosmos world model platform at CES 2025, which may spark a revolution in "Physical AI."
Will robots soon have their "ChatGPT moment"? NVIDIA will heavily release the Cosmos world model platform at CES 2025, which may spark a revolution in "Physical AI."
This platform is described as a key step to accelerate the development of "Physical AI," aiming to elevate the fields of autonomous vehicles and robots to a higher level.
Physical AI gives robots stronger environmental perception, understanding, and interaction capabilities. Advances in Physical AI will greatly promote the development of industries such as autonomous driving and robotics, which require a high level of physical scene analysis. Huang Renxun stated at the CES conference that Physical AI will fundamentally change the $50 trillion manufacturing and logistics industries, making all moving things, from cars and trucks to factories and warehouses, roboticized and driven by AI.
According to NVIDIA's official website, the Physical AI system consists of key components such as Omniverse, Cosmos, and Isaac Sim. The Cosmos platform utilizes over 20 million hours of video training data, aiming to "teach AI to understand the physical world."
What is Physical AI?
Physical AI, also known as generative physical AI, is a technology that enables autonomous machines (such as robots, self-driving cars, etc.) to perceive, understand, and execute complex operations in the real physical world.
It extends traditional generative AI to understand the spatial relationships and physical behaviors of the 3D world. In simple terms, the feedback provided by AI must comply with physical laws.
For example, text-to-image or text-to-video models, if they do not consider physics, will generate content that lacks details such as gravity and optics. After integrating physical knowledge, the generated content will be more realistic.
Jensen Huang emphasized earlier this year that 'the new wave of AI is physical AI.'
Physical AI will empower robots with stronger environmental perception, understanding, and interaction capabilities. Traditional robots can only execute tasks according to preset programs, while robots equipped with physical AI can better understand their surroundings and react accordingly based on physical laws. They can better recognize objects, predict motion trajectories, and navigate and operate in complex environments.
"Physical AI will completely change the $50 trillion manufacturing and logistics industries," Huang said at this year's CES International Consumer Electronics Show:
"From cars and trucks to factories and warehouses, everything that moves will be automated and powered by AI. NVIDIA's Omniverse Digital Twin operating system and Cosmos physical AI are the cornerstones of driving the Global digitalization of the real economy."
NVIDIA has built a complete physical AI ecosystem. According to NVIDIA's official website, the physical AI system includes key components such as Omniverse, Cosmos, and Isaac Sim.
Omniverse: Accelerating 3D content creation and physical simulation.
Omniverse is an open platform for building and connecting 3D worlds. It provides a range of tools, APIs, and SDKs that enable developers to easily create high-fidelity, physics-based virtual environments for training and testing AI models.
At the core of Omniverse is the Universal Scene Description (OpenUSD), which allows for data interoperability between different 3D tools. This release of Omniverse has also been further expanded; for example, the generative AI models powered by NVIDIA Edify SimReady can automatically add physical effects or material attributes to existing 3D Assets, greatly accelerating the creation and preparation process of 3D content.
SWHY states that in NVIDIA’s vision for the future, the development of robotics relies on three core computers.
One is used for training AI, another for controlling the test AI in the physical simulation environment, and a third is a simulated environment computer installed inside the robot or Smart Automobile, supporting physical AI algorithms.
One of the currently applied scenarios is to verify the reliability of program logic in the simulation environment; the second is to obtain data that is difficult to acquire from the real world to continuously train AI models. Currently, many large companies are adopting this method. From a Software perspective, Ansys, a leading company in the simulation field, allows access to its simulation products through NVIDIA's Omniverse, enhancing NVIDIA DRIVE's high-fidelity and scalable 3D environment using Ansys's physics solvers oriented towards Cameras, Lidar, and Radar Sensors, which is crucial for the development of autonomous driving systems.
In this way, all data during the future driving process can be fed back in real-time for decision-making, while generating more similar data to simulate more scenarios, accelerating the enhancement of training effects and breaking through the bottleneck of data acquisition.
SWHY believes that NVIDIA's significant investment in Omniverse indicates that the future direction of its computing power will mainly focus on large model AI generation, robotics, and intelligent driving fields.
Cosmos WFMs: A key step for AI to understand the physical world.
The development of Physical AI is extremely complex, requiring vast amounts of real-world data and long testing periods, with high development costs.
NVIDIA's Cosmos platform was designed to address this pain point by providing the capability to generate physical simulation data through its generative world foundation model. Cosmos WFMs allow developers to quickly generate high-fidelity data based on real physical laws, reducing the need for expensive real-world data.
During his keynote speech, Jensen Huang pointed out that the Cosmos platform utilizes over 20 million hours of video training data, aiming to 'teach AI to understand the physical world.'
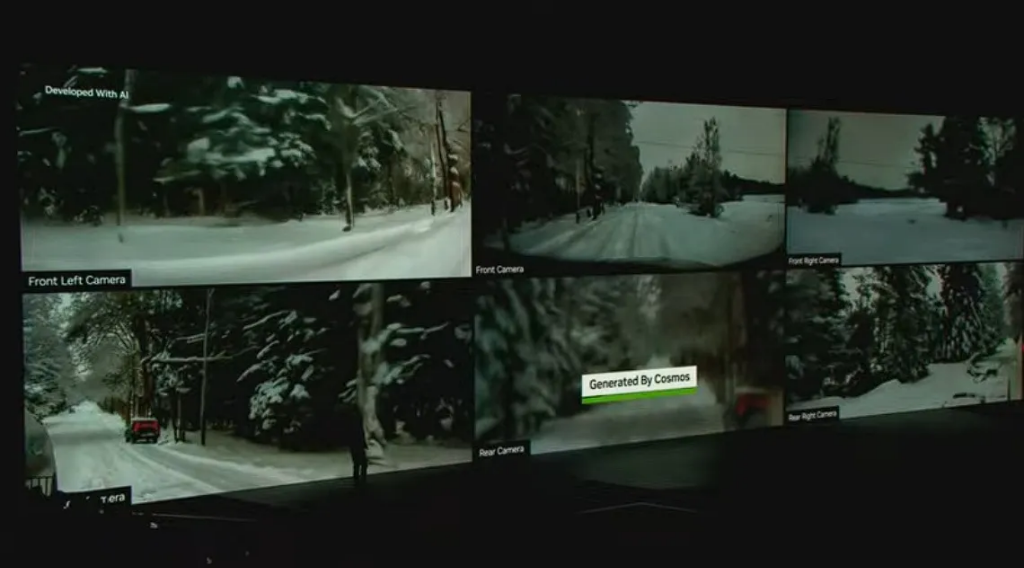
These models generate diverse physical environmental scenes, such as driving in snow or crowded warehouses, by combining text, images, videos, and robot sensor data, thus providing critical support for the development of autonomous driving and robotics.
Cosmos uses NVIDIA's NeMo Curator framework and CUDA accelerated data processing pipelines, capable of processing 20 million hours of video in just 14 days, a task that would take 3.4 years in a traditional CPU environment.
The Cosmos Tokenizer, as a state-of-the-art visual tokenization tool, can transform images and videos into efficient visual tokens, improving processing speeds by 12 times and compression efficiency by 8 times.
Jensen Huang stated, "The 'ChatGPT moment' in the field of robots is about to arrive." Just as large language models (LLMs) are driving advancements in natural language processing, Cosmos WFMs are considered fundamental tools for the development of robots and autonomous driving:
"We created Cosmos to democratize physical AI, allowing every developer access to general robotic technology."
It can be said that the launch of Cosmos completes an important link in NVIDIA's physical AI system for "understanding the world."
Multiple industry giants embrace Cosmos.
Several leading companies have become the first users of Cosmos, including 1X, Agile Robots, Waabi, Uber, and others. These companies are leveraging the Cosmos platform to drive advancements in robotics and autonomous driving technology.
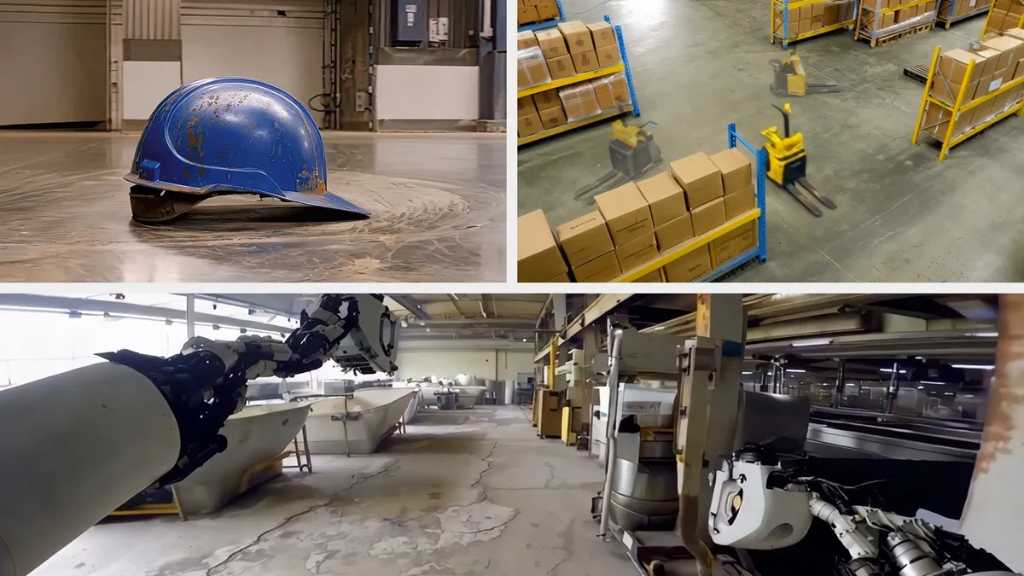

Taking Uber as an example, by integrating its rich driving data with the capabilities of the Cosmos platform and NVIDIA DGX Cloud, Uber is collaborating with NVIDIA to accelerate the development of safe and scalable autonomous driving solutions.
Uber's CEO Dara Khosrowshahi stated:
"Generative AI will power the future of mobility, which requires rich data and very powerful computing capabilities. By collaborating with NVIDIA, we believe we can help accelerate the development of safe and scalable autonomous driving solutions in the Industry."
Agility's CTO Pras Velagapudi stated in a statement:
"Data scarcity and variability are key challenges to successful learning in robotic environments. Cosmos's text, image, and video to world capabilities enable us to generate and enhance realistic scenes for various tasks, which we can use to train models without spending large amounts of costly real-world data capture."
Currently, Cosmos WFMs are available for download through NVIDIA NGC and Hugging Face platforms, allowing developers to use these models and their fine-tuning frameworks. In addition, Cosmos will achieve fast deployment through NVIDIA's DGX Cloud and provide comprehensive support for enterprise users.

 机器人即将迎来“ChatGPT时刻”?英伟达在CES 2025重磅发布Cosmos世界基础模型平台,或掀起“物理AI”革命。
机器人即将迎来“ChatGPT时刻”?英伟达在CES 2025重磅发布Cosmos世界基础模型平台,或掀起“物理AI”革命。