What Is SEC Form 10-Q?
Form 10-Q of the Securities and Exchange Commission is a detailed report of financial performance that is required to be presented to the SEC quarterly by all publicly traded corporations (SEC). As a result of running their businesses, companies are obligated to provide pertinent information about their finances that is included in the 10-Q form. In most cases, the 10-Q is not audited as part of the reporting process.
The corporation is required to submit a Form 10-Q for each of the first three quarters that make up the fiscal year.
Key Points
The SEC Form 10-Q is a thorough report on the company's financial performance filed quarterly to the Securities and Exchange Commission by all publicly traded corporations.
The most recent quarter's financial statements and management's discussion and analysis of those statements, disclosure, and internal control systems, are included in Form 10-Q.
The 10-Q forms are due 40 or 45 days after the end of each quarter for publicly traded companies, based on the size of their public float.
Form 10-Q gives investors a picture of the company's financial status, which can be compared to prior quarters and used to gauge the stock's future performance prospects.
Unlike the yearly Form 10-K that businesses are required to submit, the quarterly Form 10-Q is not an audited statement.
Understanding SEC Form 10-Q
Under federal securities rules, publicly listed corporations must disclose certain information to their shareholders and the broader public. These disclosures could occur regularly or just when certain events have occurred. Form 10-Q is one of the numerous forms required by the SEC. Following the conclusion of each quarter, a business will use it to disclose unaudited financial statements and provide a summary of the firm's current financial condition.
It is necessary to submit three 10-Q reports annually; however, the specific filing dates will differ depending on the organization's fiscal year.
The 10-Q is unnecessary for the fourth and final quarter of the year: Rather than filing its quarterly reports after the fourth quarter, a corporation will instead submit its annual report using Form 10-K. In contrast to the 10-Q, this report is audited and tends to include more information than that report. [1]
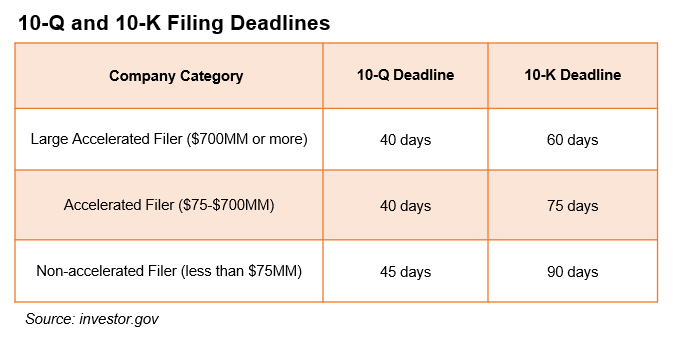
SEC Form 10-Q Filing Deadlines
The date by which a firm is required to submit a Form 10-Q varies and is determined by the total number of shares that are still outstanding.
Any business that files a 10-Q will be placed into one of three groups. The proportion of the company's outstanding stock owned by members of the general public, as opposed to officials, owners, or the government, is known as the public float, which is used to classify the company. In its basic form, the float comprises all of a corporation's freely traded common stock shares.
Large accelerated filers are often reserved for the world's largest corporations. To fulfill this condition, the organizations need to have a public float of at least 700 million dollars. If the corporation can fulfill this criterion, it will have forty days from the end of the quarter before it is required to submit its 10-Q.
Businesses with a public float of at least $75 million but less than $700 million qualify for accelerated processing. The 10-Q must also be submitted within 40 days for accelerated filers.
Companies with a market capitalization of less than $75 million are considered non-accelerated filers. These businesses have a deadline of 45 calendar days after the end of each quarter to submit their 10-Q reports.
Failure to Meet Form 10-Q Filing Deadline
A corporation must utilize a non-timely (NT) filing when it cannot submit its 10-Q by the deadline for submission. An NT filing must include an explanation as to why the deadline was not met, and it provides the corporation with a further five days to complete the filing. Businesses must file an NT 10-Q to make a request for an extension and provide an explanation for the delay.
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) will accept companies' late filings if they can justify their actions within a certain amount of time. Companies sometimes miss their filing deadlines for various reasons, including mergers and acquisitions (M&A), corporate litigation, a continuing assessment by corporate auditors, or the lasting impact of a previous bankruptcy filing.
If a 10-Q filing is submitted within the specified time frame, it will be considered submitted on time. If this newly extended deadline is not adhered to, there will be consequences, some of which include the possible cancellation of the SEC registration, exclusion from stock exchanges, and legal repercussions.
Components of SEC Form 10-Q
A 10-Q filing is comprised of two separate components. The report's first section covers all the pertinent financial information for the period. This comprises disclosures addressing market risk and internal controls, condensed financial statements, management discussion, and analysis of the financial status of the business.
The second section includes anything else that is relevant to the topic. This comprises legal procedures, unregistered sales of equity securities, the utilization of profits from the sale of registration sales of equity, and failures upon senior securities. Also included in this category is the use of funds from the sale of unregistered sales of equity. In this area, the corporation will provide any further information, including the use of exhibits, if applicable. [2]
Importance of SEC Form 10-Q
The 10-Q gives investors an overview of the company's current financial situation. Shareholders could use the form to better understand the company's quarterly profits and other aspects of its operations and compare these aspects to those of earlier quarters, allowing them to follow the company's success.
Investors usually find out about changes to cash flow and/or accounts receivable, variables impacting a company's inventory, share buybacks, and legal risks in the 10-Q.
You can evaluate a firm's performance in which you already have investments or are contemplating investing by comparing it to the information included in the 10-Q of a close rival. This will give you an understanding of whether or not it is a good option, the areas in which it is lacking, and how it has room for improvement.
What Is a 10-Q Filing?
A report known as a 10-Q filing is something that the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) requires all publicly traded corporations to produce after the conclusion of each of their first three fiscal quarters (hence the "Q"). Form 10-Q must be filled out to make the filing submission.
What Is the Difference Between a 10-K and a 10-Q?
The number of details included on Forms 10-K and 10-Q, as well as the regularity with which they must be filed, are the primary factors that differentiate the two. A company's annual report, known as a Form 10-K, needs to submit after the close of its fiscal year. This report, which is only submitted once, compiles a summary of all of the year's information, including the fourth quarter's information. In contrast, a corporation needs to submit a Form 10-Q after each fiscal quarter, which occurs three times every year. It provides information on finances for the given quarter. Additionally, Form 10-K is a report that has been audited. Form 10-Q is not often required.
Moomoo trading app will provide the earnings report calendar feature, so traders and investors can track the earnings report schedule more quickly with convenience. Sign up and download the moomoo app today to access the clear and customizable earnings calendar!
Images provided are not current and any securities are shown for illustrative purposes only.
[1] https://www.investor.gov/introduction-investing/investing-basics/glossary/form-10-q
[2] https://www.sec.gov/files/form10-q.pdf