Margin Trading: How It Works, Risks and Benefits
Buying on margin refers to borrowing money from a broker to purchase stock. With a margin account, investors can boost their financial leverage by using someone else's money. Indeed, margin trading is a great alternative to traditional trading. It also brings many risks.
Buying on margin also boosts the loss effects. Purchasing stocks on margin amplifies the impact of losses. Besides, there're also chances of a margin call. In this case, you may require additional money to maintain your investment and liquidate your position.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
•Buying stocks on margin refers to borrowing money to purchase stock shares and securities.
•Trading on margin allows investors to use leverage to maintain or boost their position.
•Trading on margin involves risk because it requires traders to pay the money back to the broker.
•Buying on margin can amplify both losses and gains.
•Too much drop in the account market value leads to a margin call. As a result, investors have to deposit more cash or sell their shares.
How Buying Stocks on Margin Works
Typically, brokers pay the investors through their brokerage account. When an investor buys a stock, cash is debited from their brokerage account to pay for the purchase.
Based on the number of shares and stock price, investors can buy 100% of their stock with cash.
Margin trading refers to borrowing money from a broker to purchase equity shares and securities.
Investors can also buy more stock than they could once they have taken out a loan. Investors have to pay a specific interest on the loan amount to leverage these benefits.
Establishing a margin account is necessary for a margin account. This account is distinct from the standard cash account. The stocks or assets kept in the margin account serve as security for the margin loan. Not all securities, nevertheless, can be bought on margin.
Minimum Margin
Trading on margin requires investors to deposit a minimum margin with their brokerage firm. The minimum margin is $2000 or 100% of the purchase price. The minimum margin could also be higher than $2000 for some firms. [1]
Initial Margin
Federal Reserve set a limiting value for the amount to be borrowed. This limiting value is known as the initial margin.
An investor can borrow up to 50% of the total stock price. They can then use this borrowed money to purchase new stocks. It means you need to deposit 50% to the broker if you want to borrow 50% of the stock amount. Some brokerage firms also require you to submit more than 50% of the stock price. [2]
Margin History
The margin requirement was just 10% before the Stock Market Crash in 1929. An investor could buy stocks worth $100,000 if they have a $10,000 balance in their account.
As a result, investors enjoyed a dramatic boost in leverage. But a sudden stock market crash causes them to lose all their money. Margin investing was therefore discouraged. Additionally, some Federal reserved board stock speculation leads to the wastage of resources. [3]
Example of Buying Stocks on Margin
Suppose you want to purchase stocks worth $10,000 more than the amount present in your margin account. You need to have at least 50% cash amount as an initial 50% margin requirement.
However, it will allow you to double your purchasing power, enabling you to buy stock worth $20,000.
Once you have bought the stock with the money borrowed, two scenarios could happen:
Scenario 1: The Stock Price Rises
The first scenario will help you understand how purchasing on margin could increase the gains.
Suppose you want to purchase stock worth $20,000. After purchasing stock worth $20,000, you owe the broker $10,000. Now, suppose the stock's price increases; the following scenarios could happen:
•Buy Stocks of worth $20,000; finance of $10,000 in cash and $10,000 via a margin loan
•Increase in stock market value to $30,000
•Stock price moves higher; new market value = $30,000
•Sell the stock at the new market value
•Pay the loan+interest from the profit
•The account balance will be $20,000
It indicates that investors have earned 100% profit on an investment of $10,000. Had you initially paid for the entire $20,000 with cash (no margin loan) and sold at $30,000, the gain would be only 50%.
Scenario 2: Sudden Fall in Stock Price
A fall in stock price could amplify the losses in the same way a rise in stock price amplifies the gains.
Let's imagine you have the same amount of stock. But stock price drops instead of rising.
•Buy Stocks of worth $20,000; finance of $10,000 in cash and $10,000 via a margin loan
•The decline in stock market value to $15,000
•Sell the stock at the new market value
•Pay the loan+interest from the profit
•The account balance will be $5,000
So, your new account balance will be $5,000. To conclude, you've lost 50% on your initial investment on the stock's market value decline of only 25%.
Why Buying Stocks on Margin Can Be Risky
Investment in any form comes with risks. Margin trading boosts the chances of these risks.
Maintenance Margin
Your margin account needs to include a minimum amount of equity after you've purchased the stock on margin. Equity refers to the stock's market value, excluding the margin loan amount.
According to the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), investors need to own at least 25% of the entire market value of the securities. [4]
The requirement for maintenance margin could be different for different brokers. Some brokers charge 30-40%.
There is not much risk involved in the maintenance margin of 25%. However, the decline in the market value of securities may run the investors into financial trouble.
Margin Calls
If the decline in stock price causes your equity to drop below the maintenance margin, it may lead to a margin call. As a result, investors have to liquidate stock to increase equity. Additionally,
they may also have to deposit additional cash.
•Suppose your broker demands a 40% maintenance margin instead of a 25% FINRA requirement, then
•You purchased the stock of worth $20,000 with $10,000 borrowed on margin.
•The decline in stock price to $15,000 leads the equity to decline to $5,000.
•Equity refers to total security value - margin loan. So, in the current scenario, it would be $15,000-$10,000= 5,000.
•Equity is 33% of the stock's market value in this case. So, the current equity is less than 40%.
•Your broker could sell your stock without your consent if you don't want to deposit extra money to cover the margin call.
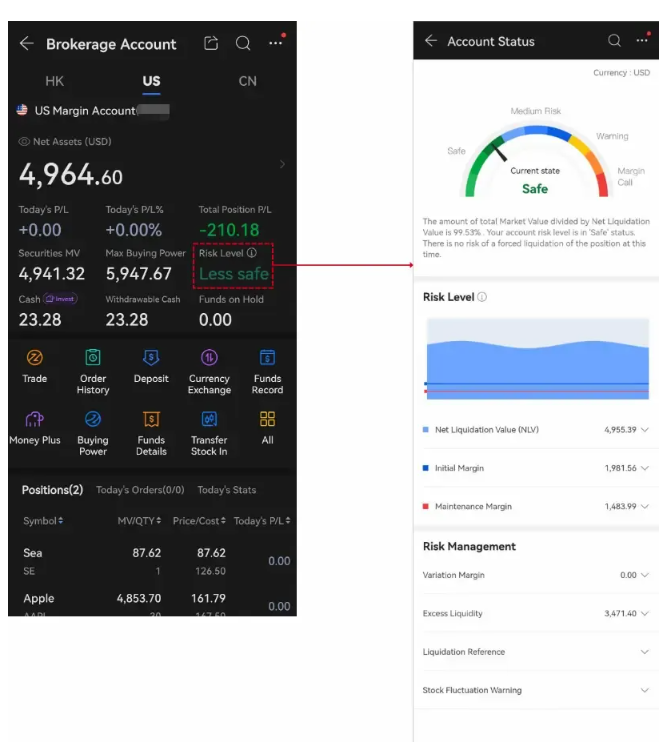
moomoo app discloses the risks on the user's account risk details page. It will contain descriptions of your account risks, disposal suggestions, and early warning information on fluctuations of
individual stocks. You could easily find out the risk level of the stock when you do margin trading and be better informed of the dangers in the early stage.
What does buying stock on margin mean?
Buying stocks on margin refers to borrowing money from brokers to buy stocks. Margin loans allow investors to purchase more stock than their buying power.
How does margin trading work on stocks?
To buy stocks on margin, you need to open a margin account first. Then you need to get approval for the loan.
Investors can sell the stock once the stock's market value rises. After paying the loan, they could then keep the gains. On the other hand, a decrease in the stock's price could lead to a margin call.
A margin call requires you to sell the stock at a loss or deposit more cash. Whatever the scenario, you need to repay the broker's loan.
[1] SEC.gov | Margin: Borrowing Money to Pay for Stocks
[2] Federal Register: Request Access